Case control study of women treated with chemotherapy for breast cancer during pregnancy as compared with nonpregnant patients with breast cancer
- PMID: 23576478
- PMCID: PMC3639522
- DOI: 10.1634/theoncologist.2012-0340
Case control study of women treated with chemotherapy for breast cancer during pregnancy as compared with nonpregnant patients with breast cancer
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this analysis was to compare disease-free survival (DFS), progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS) between pregnant and nonpregnant patients with breast cancer.
Methods: From 1989 to 2009, 75 women were treated with chemotherapy during pregnancy. Each pregnant case was matched on age and cancer stage to two nonpregnant patients with breast cancer (controls). Fisher's exact test, the Kaplan-Meier method, and Cox proportional hazards regression models were used.
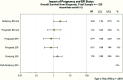
Results: Median follow-up time for patients who were alive at the end of follow-up (n = 159) was 4.20 years (range: 0.28-19.94 years). DFS at 5 years was 72% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 58.3%-82.1%) for pregnant patients and 57% (95% CI: 46.7%-65.8%) for controls (p = .0115). Five-year PFS was 70% (95% CI: 56.8%-80.3%) for pregnant patients and 59% (95% CI: 49.1%-67.5%) for controls (p = .0252). Five-year OS was 77% (95% CI: 63.9%-86.4%) for pregnant patients and 71% (95% CI: 61.1%-78.3%) for controls (p = .0461). Hazard ratio estimates favored improved survival for pregnant patients in univariate analyses and multivariate analyses, controlling for age, year of diagnosis, stage, and tumor grade.
Conclusions: For patients who received chemotherapy during pregnancy, survival was comparable to-if not better than-that of nonpregnant women. Pregnant patients with breast cancer should receive appropriate local and systemic therapy for breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures of potential conflicts of interest may be found at the end of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Smith LH, Dalrymple JL, Leiserowitz GS, et al. Obstetrical deliveries associated with maternal malignancy in California, 1992 through 1997. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2011;184:1504–1512. - PubMed
-
- Andersson TM, Johansson AL, Hsieh CC, et al. Increasing incidence of pregnancy-associated breast cancer in Sweden. Obstet Gynecol. 2009;114:568–572. - PubMed
-
- Ribeiro G, Jones DA, Jones M. Carcinoma of the breast associated with pregnancy. Br J Surg. 1986;73:607–609. - PubMed
-
- Bonnier P, Romain S, Dilhuydy JM, et al. Influence of pregnancy on the outcome of breast cancer: A case-control study. Int J Cancer. 1997;72:720–727. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

