Hedgehog signaling alters reliance on EGF receptor signaling and mediates anti-EGFR therapeutic resistance in head and neck cancer
- PMID: 23576557
- PMCID: PMC3674118
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4047
Hedgehog signaling alters reliance on EGF receptor signaling and mediates anti-EGFR therapeutic resistance in head and neck cancer
Abstract
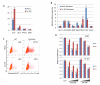
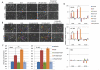
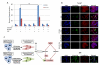
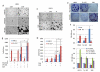
The EGF receptor (EGFR)-directed monoclonal antibody cetuximab is the only targeted therapy approved for the treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (HNSCC) but is only effective in a minority of patients. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) has been implicated as a drug resistance mechanism in multiple cancers, and the EGFR and Hedgehog pathways (HhP) are relevant to this process, but the interplay between the two pathways has not been defined in HNSCC. Here, we show that HNSCC cells that were naturally sensitive to EGFR inhibition over time developed increased expression of the HhP transcription factor GLI1 as they became resistant after long-term EGFR inhibitor exposure. This robustly correlated with an increase in vimentin expression. Conversely, the HhP negatively regulated an EGFR-dependent, EMT-like state in HNSCC cells, and pharmacologic or genetic inhibition of HhP signaling pushed cells further into an EGFR-dependent phenotype, increasing expression of ZEB1 and VIM. In vivo treatment with cetuximab resulted in tumor shrinkage in four of six HNSCC patient-derived xenografts; however, they eventually regrew. Cetuximab in combination with the HhP inhibitor IPI-926 eliminated tumors in two cases and significantly delayed regrowth in the other two cases. Expression of EMT genes TWIST and ZEB2 was increased in sensitive xenografts, suggesting a possible resistant mesenchymal population. In summary, we report that EGFR-dependent HNSCC cells can undergo both EGFR-dependent and -independent EMT and HhP signaling is a regulator in both processes. Cetuximab plus IPI-926 forces tumor cells into an EGFR-dependent state, delaying or completely blocking tumor recurrence.
©2013 AACR.
Figures

Similar articles
-
mTOR co-targeting in cetuximab resistance in head and neck cancers harboring PIK3CA and RAS mutations.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014 Aug 5;106(9):dju215. doi: 10.1093/jnci/dju215. Print 2014 Sep. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014. PMID: 25099740 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical modeling of EGFR inhibitor resistance in head and neck cancer.Cancer Biol Ther. 2012 Aug;13(10):935-45. doi: 10.4161/cbt.20846. Epub 2012 Aug 1. Cancer Biol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22785204 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Stat3 abrogates EGFR inhibitor resistance in cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Sep 15;18(18):4986-96. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0792. Epub 2012 Jul 23. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22825581 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular targeted therapies in the management of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: recent developments and perspectives.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013 Mar;13(3):389-402. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23092267 Review.
-
Molecular pathways in head and neck cancer: EGFR, PI3K, and more.Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2013:246-55. doi: 10.14694/EdBook_AM.2013.33.246. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2013. PMID: 23714515 Review.
Cited by
-
Transient Activation of Hedgehog Signaling Inhibits Cellular Senescence and Inflammation in Radiated Swine Salivary Glands through Preserving Resident Macrophages.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 16;22(24):13493. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413493. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948290 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation dose uncertainty and correction for a mouse orthotopic and xenograft irradiation model.Int J Radiat Biol. 2016;92(1):50-6. doi: 10.3109/09553002.2016.1114189. Epub 2015 Dec 21. Int J Radiat Biol. 2016. PMID: 26689828 Free PMC article.
-
The programmed death ligand 1 interactome demonstrates bidirectional signaling coordinating immune suppression and cancer progression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2023 Nov 8;115(11):1392-1403. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djad126. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2023. PMID: 37389416 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of GLI1 in vincristine-resistant rhabdomyosarcoma and Ewing sarcoma.BMC Cancer. 2020 Jun 3;20(1):511. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-06985-0. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32493277 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Hedgehog Pathway in Cancer: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives.Cells. 2019 Feb 12;8(2):153. doi: 10.3390/cells8020153. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30759860 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:10–29. - PubMed
-
- Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J, Azarnia N, Shin DM, Cohen RB, et al. Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. The New England journal of medicine. 2006;354:567–78. - PubMed
-
- Vermorken JB, Mesia R, Rivera F, Remenar E, Kawecki A, Rottey S, et al. Platinum-based chemotherapy plus cetuximab in head and neck cancer. The New England journal of medicine. 2008;359:1116–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

