Inhibition of c-Met reduces lymphatic metastasis in RIP-Tag2 transgenic mice
- PMID: 23576559
- PMCID: PMC3686901
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2160
Inhibition of c-Met reduces lymphatic metastasis in RIP-Tag2 transgenic mice
Abstract
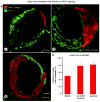
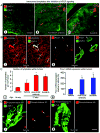
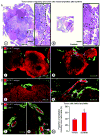
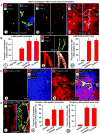
Inhibition of VEGF signaling can promote lymph node metastasis in preclinical models, but the mechanism is not fully understood, and successful methods of prevention have not been found. Signaling of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and its receptor c-Met can promote the growth of lymphatics and metastasis of some tumors. We sought to explore the contributions of c-Met signaling to lymph node metastasis after inhibition of VEGF signaling. In particular, we examined whether c-Met is upregulated in lymphatics in or near pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors in RIP-Tag2 transgenic mice and whether lymph node metastasis can be reduced by concurrent inhibition of VEGF and c-Met signaling. Inhibition of VEGF signaling by anti-VEGF antibody or sunitinib in mice from the age of 14 to 17 weeks was accompanied by more intratumoral lymphatics, more tumor cells inside lymphatics, and more lymph node metastases. Under these conditions, lymphatic endothelial cells, like tumor cells, had strong immunoreactivity for c-Met and phospho-c-Met. c-Met blockade by the selective inhibitor, PF-04217903, significantly reduced metastasis to local lymph nodes. Together, these results indicate that inhibition of VEGF signaling in RIP-Tag2 mice upregulates c-Met expression in lymphatic endothelial cells, increases the number of intratumoral lymphatics and number of tumor cells within lymphatics, and promotes metastasis to local lymph nodes. Prevention of lymph node metastasis by PF-04217903 in this setting implicates c-Met signaling in tumor cell spread to lymph nodes.
©2013 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
J. Christensen: employee of Pfizer Global Research and Development. D.M. McDonald: research funding from a grant to University of California- San Francisco from Pfizer Global Research and Development. The other authors had no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
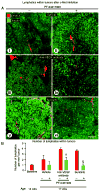
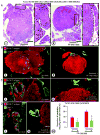
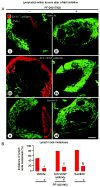
References
-
- Cao Y. Opinion: emerging mechanisms of tumour lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:735–43. - PubMed
-
- Skobe M, Hawighorst T, Jackson DG, Prevo R, Janes L, Velasco P, et al. Induction of tumor lymphangiogenesis by VEGF-C promotes breast cancer metastasis. Nat Med. 2001;7:192–8. - PubMed
-
- Stacker SA, Caesar C, Baldwin ME, Thornton GE, Williams RA, Prevo R, et al. VEGF-D promotes the metastatic spread of tumor cells via the lymphatics. Nat Med. 2001;7:186–91. - PubMed
-
- Casanovas O, Hicklin DJ, Bergers G, Hanahan D. Drug resistance by evasion of antiangiogenic targeting of VEGF signaling in late-stage pancreatic islet tumors. Cancer Cell. 2005;8:299–309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

