Threshold levels of ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitors retained in chronic myeloid leukemia cells determine their commitment to apoptosis
- PMID: 23576564
- PMCID: PMC3674150
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3904
Threshold levels of ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitors retained in chronic myeloid leukemia cells determine their commitment to apoptosis
Abstract
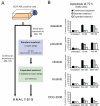
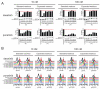
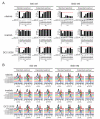
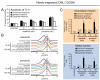
The imatinib paradigm in chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) established continuous BCR-ABL inhibition as a design principle for ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI). However, clinical responses seen in patients treated with the ABL TKI dasatinib despite its much shorter plasma half-life and the apparent rapid restoration of BCR-ABL signaling activity following once-daily dosing suggested acute, potent inhibition of kinase activity may be sufficient to irrevocably commit CML cells to apoptosis. To determine the specific requirements for ABL TKI-induced CML cell death for a panel of clinically important ABL TKIs (imatinib, nilotinib, dasatinib, ponatinib, and DCC-2036), we interrogated response of CML cell lines and primary CML cells following acute drug exposure using intracellular fluorescence-activated cell sorting and immunoblot analyses of BCR-ABL signaling, apoptosis measurements, liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry of intracellular drug levels, and biochemical TKI dissociation studies. Importantly, significant intracellular TKI stores were detected following drug washout, levels of which tracked with onset of apoptosis and incomplete return of BCR-ABL signaling, particularly pSTAT5, to baseline. Among TKIs tested, ponatinib showed the most robust capacity for apoptotic commitment showing sustained suppression of BCR-ABL signaling even at low intracellular levels following extensive washout, consistent with high-affinity binding and slow dissociation from ABL kinase. Together, our findings suggest commitment of CML cells to apoptosis requires protracted incomplete restoration of BCR-ABL signaling mediated by intracellular retention of TKIs above a quantifiable threshold. These studies refine our understanding of apoptotic commitment in CML cells and highlight parameters important to design of therapeutic kinase inhibitors for CML and other malignancies.
©2013 AACR.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Apoptosis in chronic myeloid leukemia cells transiently treated with imatinib or dasatinib is caused by residual BCR-ABL kinase inhibition.Am J Hematol. 2013 May;88(5):385-93. doi: 10.1002/ajh.23419. Epub 2013 Mar 27. Am J Hematol. 2013. PMID: 23420553
-
All tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant chronic myelogenous cells are highly sensitive to ponatinib.Oncotarget. 2012 Dec;3(12):1557-65. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.692. Oncotarget. 2012. PMID: 23238683 Free PMC article.
-
Cotreatment with vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid) enhances activity of dasatinib (BMS-354825) against imatinib mesylate-sensitive or imatinib mesylate-resistant chronic myelogenous leukemia cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Oct 1;12(19):5869-78. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0980. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 17020995
-
Suppression of autophagy by BCR/ABL.Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2012 Jan 1;4(2):453-60. doi: 10.2741/278. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2012. PMID: 22202070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Bcr-Abl inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia: keeping resistance in check.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2008 Jun;17(6):865-78. doi: 10.1517/13543784.17.6.865. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2008. PMID: 18491988 Review.
Cited by
-
Response and Resistance to BCR-ABL1-Targeted Therapies.Cancer Cell. 2020 Apr 13;37(4):530-542. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.03.006. Cancer Cell. 2020. PMID: 32289275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sustained inhibition of STAT5, but not JAK2, is essential for TKI-induced cell death in chronic myeloid leukemia.Leukemia. 2015 Jan;29(1):76-85. doi: 10.1038/leu.2014.156. Epub 2014 May 12. Leukemia. 2015. PMID: 24813920
-
KIT signaling governs differential sensitivity of mature and primitive CML progenitors to tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Cancer Res. 2013 Sep 15;73(18):5775-86. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1318. Epub 2013 Jul 25. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23887971 Free PMC article.
-
Kinase inhibitor therapy in CML: it's what's inside that counts.Oncotarget. 2013 Sep;4(9):1332-3. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1271. Oncotarget. 2013. PMID: 23934763 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Prolonged cellular midostaurin retention suggests potential alternative dosing strategies for FLT3-ITD-positive leukemias.Leukemia. 2016 Oct;30(10):2090-2093. doi: 10.1038/leu.2016.127. Epub 2016 May 3. Leukemia. 2016. PMID: 27137475 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Shah NP, Tran C, Lee FY, Chen P, Norris D, Sawyers CL. Overriding imatinib resistance with a novel ABL kinase inhibitor. Science. 2004;305:399–401. - PubMed
-
- Weisberg E, Manley PW, Breitenstein W, Bruggen J, Cowan-Jacob SW, Ray A, et al. Characterization of AMN107, a selective inhibitor of native and mutant Bcr-Abl. Cancer cell. 2005;7:129–41. - PubMed
-
- O’Hare T, Zabriskie MS, Eiring AM, Deininger MW. Pushing the limits of targeted therapy in chronic myeloid leukaemia. Nature reviews Cancer. 2012;12:513–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

