Kelch-like 3 and Cullin 3 regulate electrolyte homeostasis via ubiquitination and degradation of WNK4
- PMID: 23576762
- PMCID: PMC3651502
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1304592110
Kelch-like 3 and Cullin 3 regulate electrolyte homeostasis via ubiquitination and degradation of WNK4
Abstract
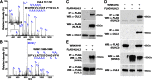
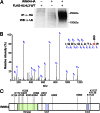
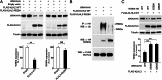
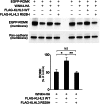
Pseudohypoaldosteronism type II (PHAII) is a rare Mendelian syndrome featuring hypertension and hyperkalemia resulting from constitutive renal salt reabsorption and impaired K(+) secretion. Recently, mutations in Kelch-like 3 (KLHL3) and Cullin 3 (CUL3), components of an E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, were found to cause PHAII, suggesting that loss of this complex's ability to target specific substrates for ubiquitination leads to PHAII. By MS and coimmunoprecipitation, we show that KLHL3 normally binds to WNK1 and WNK4, members of WNK (with no lysine) kinase family that have previously been found mutated in PHAII. We show that this binding leads to ubiquitination, including polyubiquitination, of at least 15 specific sites in WNK4, resulting in reduced WNK4 levels. Dominant disease-causing mutations in KLHL3 and WNK4 both impair WNK4 binding, ubiquitination, and degradation. WNK4 normally induces clearance of the renal outer medullary K(+) channel (ROMK) from the cell surface. We show that WT but not mutant KLHL3 inhibits WNK4-induced reduction of ROMK level. We show that PHAII-causing mutations in WNK4 lead to a marked increase in WNK4 protein levels in the kidney in vivo. These findings demonstrate that CUL3-RING (really interesting new gene) ligases that contain KLHL3 target ubiquitination of WNK4 and thereby regulate WNK4 levels, which in turn regulate levels of ROMK. These findings reveal a specific role of CUL3 and KLHL3 in electrolyte homeostasis and provide a molecular explanation for the effects of disease-causing mutations in both KLHL3 and WNK4.
Keywords: Gordon syndrome; Kir1.1; proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
Control of electrolyte balance through ubiquitination.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 May 7;110(19):7535-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1305242110. Epub 2013 Apr 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23613582 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The CUL3-KLHL3 E3 ligase complex mutated in Gordon's hypertension syndrome interacts with and ubiquitylates WNK isoforms: disease-causing mutations in KLHL3 and WNK4 disrupt interaction.Biochem J. 2013 Apr 1;451(1):111-22. doi: 10.1042/BJ20121903. Biochem J. 2013. PMID: 23387299 Free PMC article.
-
Kelch-like 3/Cullin 3 ubiquitin ligase complex and WNK signaling in salt-sensitive hypertension and electrolyte disorder.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2016 Sep;31(9):1417-24. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfv259. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2016. PMID: 26152401 Review.
-
Impaired degradation of WNK1 and WNK4 kinases causes PHAII in mutant KLHL3 knock-in mice.Hum Mol Genet. 2014 Oct 1;23(19):5052-60. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu217. Epub 2014 May 12. Hum Mol Genet. 2014. PMID: 24821705
-
Decrease of WNK4 ubiquitination by disease-causing mutations of KLHL3 through different molecular mechanisms.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Sep 13;439(1):30-4. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.08.035. Epub 2013 Aug 17. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23962426
-
Regulation of blood pressure and renal electrolyte balance by Cullin-RING ligases.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2014 Sep;23(5):487-93. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000049. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2014. PMID: 24992566 Review.
Cited by
-
A narrative review of Hyporeninemic hypertension-an indicator for monogenic forms of hypertension.Pediatr Med. 2022 May;5:21. doi: 10.21037/pm-21-48. Epub 2022 May 28. Pediatr Med. 2022. PMID: 36325202 Free PMC article.
-
Blood pressure effects of sodium transport along the distal nephron.Kidney Int. 2022 Dec;102(6):1247-1258. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2022.09.009. Epub 2022 Oct 10. Kidney Int. 2022. PMID: 36228680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distal convoluted tubule.Compr Physiol. 2015 Jan;5(1):45-98. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c140002. Compr Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25589264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elevated intracellular Na+ and osmolarity stimulate catalytic activity of the ubiquitin ligase Nedd4-2.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jul 26;119(30):e2122495119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2122495119. Epub 2022 Jul 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35858421 Free PMC article.
-
WNK4 kinase is a physiological intracellular chloride sensor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Mar 5;116(10):4502-4507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1817220116. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30765526 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lifton RP, et al. A chimaeric 11 beta-hydroxylase/aldosterone synthase gene causes glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism and human hypertension. Nature. 1992;355(6357):262–265. - PubMed
-
- Kahle KT, Ring AM, Lifton RP. Molecular physiology of the WNK kinases. Annu Rev Physiol. 2008;70:329–355. - PubMed
-
- Wilson FH, et al. Human hypertension caused by mutations in WNK kinases. Science. 2001;293(5532):1107–1112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

