Current perspectives in NSAID-induced gastropathy
- PMID: 23576851
- PMCID: PMC3610380
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/258209
Current perspectives in NSAID-induced gastropathy
Abstract
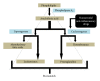
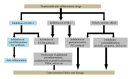
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are the most highly prescribed drugs in the world. Their analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic actions may be beneficial; however, they are associated with severe side effects including gastrointestinal injury and peptic ulceration. Though several approaches for limiting these side effects have been adopted, like the use of COX-2 specific drugs, comedication of acid suppressants like proton pump inhibitors and prostaglandin analogs, these alternatives have limitations in terms of efficacy and side effects. In this paper, the mechanism of action of NSAIDs and their critical gastrointestinal complications have been reviewed. This paper also provides the information on different preventive measures prescribed to minimize such adverse effects and analyses the new suggested strategies for development of novel drugs to maintain the anti-inflammatory functions of NSAIDs along with effective gastrointestinal protection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug gastropathy: causes and treatment.Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1996;220:124-7. doi: 10.3109/00365529609094763. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1996. PMID: 8898449 Review.
-
[Secondary and primary prophylaxis of gastropathy associated with nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs or low-dose-aspirin: a review based on four clinical scenarios].Z Gastroenterol. 2003 Aug;41(8):719-28. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-41208. Z Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12910426 Review. German.
-
[Recommendation for the prevention and treatment of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastrointestinal ulcers and its complications].Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2017 Jan 1;56(1):81-85. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1426.2017.01.021. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28056333 Chinese.
-
From peptic ulcer disease to NSAID gastropathy. An evolving nosology.Drugs Aging. 1995 May;6(5):358-67. doi: 10.2165/00002512-199506050-00003. Drugs Aging. 1995. PMID: 7647425 Review.
-
[The role of anti-ulcerative drugs in treatment and prevention of gastropathies induced by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs].Vnitr Lek. 2004 Nov;50(11):858-66. Vnitr Lek. 2004. PMID: 15648967 Review. Czech.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase or genetic deletion reduces diclofenac-induced gastric ulcers.Life Sci. 2017 Jul 1;180:114-122. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2017.05.018. Epub 2017 May 15. Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28522175 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of long-term results of pathogenetic treatment of Helicobacter pylori-associated gastroduodenopathies induced by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in patients with osteoarthritis.J Med Life. 2021 Mar-Apr;14(2):176-180. doi: 10.25122/jml-2020-0176. J Med Life. 2021. PMID: 34104240 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cross-Sectional Study for Prevalence of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug-Induced Gastrointestinal, Cardiac and Renal Complications in India: Interim Report.Gastroenterology Res. 2015 Aug;8(3-4):216-221. doi: 10.14740/gr658w. Epub 2015 Jul 22. Gastroenterology Res. 2015. PMID: 27785299 Free PMC article.
-
Ibuprofen-Induced Multiple Fixed Drug Eruption Confirmed by Re-Challenge: A Case Report and Literature Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Dec 28;15(1):48. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15010048. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39795576 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin: A Potent Protectant against Esophageal and Gastric Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 24;20(6):1477. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061477. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30909623 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vane JR. The mode of action of aspirin and similar compounds. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 1976;58(6):691–712. - PubMed
-
- Vane JR. The fight against rheumatism: from willow bark to COX-1 sparing drugs. Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology. 2000;51(4):573–586. - PubMed
-
- Nuki G. Pain control and the use of non-steroidal analgesic anti-inflammatory drugs. British Medical Bulletin. 1990;46(1):262–278. - PubMed
-
- Smalley WE, Ray WA, Daugherty JR, Griffin MR. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and the incidence of hospitalizations for peptic ulcer disease in elderly persons. American Journal of Epidemiology. 1995;141(6):539–545. - PubMed
-
- DeRuiter J. Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) Principles of Drug Action. 2002;2:1–25.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials