Regulation of zebrafish sleep and arousal states: current and prospective approaches
- PMID: 23576957
- PMCID: PMC3620505
- DOI: 10.3389/fncir.2013.00058
Regulation of zebrafish sleep and arousal states: current and prospective approaches
Abstract
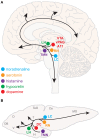
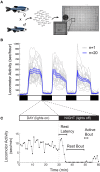
Every day, we shift among various states of sleep and arousal to meet the many demands of our bodies and environment. A central puzzle in neurobiology is how the brain controls these behavioral states, which are essential to an animal's well-being and survival. Mammalian models have predominated sleep and arousal research, although in the past decade, invertebrate models have made significant contributions to our understanding of the genetic underpinnings of behavioral states. More recently, the zebrafish has emerged as a promising model system for sleep and arousal research. Here we review experimental evidence that the zebrafish, a diurnal vertebrate, exhibits fundamental behavioral and neurochemical characteristics of mammalian sleep and arousal. We also propose how specific advantages of the zebrafish can be harnessed to advance the field. These include tractable genetics to identify and manipulate molecular and cellular regulators of behavioral states, optical transparency to facilitate in vivo observation of neural structure and function, and amenability to high-throughput drug screens to discover novel therapies for neurological disorders.
Keywords: arousal; hypocretin; neuromodulator; orexin; sleep; zebrafish.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

