The effects of propofol on local field potential spectra, action potential firing rate, and their temporal relationship in humans and felines
- PMID: 23576977
- PMCID: PMC3620583
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2013.00136
The effects of propofol on local field potential spectra, action potential firing rate, and their temporal relationship in humans and felines
Abstract
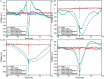
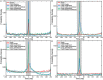
Propofol is an intravenous sedative hypnotic, which, acting as a GABAA agonist, results in neocortical inhibition. While propofol has been well studied at the molecular and clinical level, less is known about the effects of propofol at the level of individual neurons and local neocortical networks. We used Utah Electrode Arrays (UEAs) to investigate the effects of propofol anesthesia on action potentials (APs) and local field potentials (LFPs). UEAs were implanted into the neocortex of two humans and three felines. The two human patients and one feline received propofol by bolus injection, while the other two felines received target-controlled infusions. We examined the changes in LFP power spectra and AP firing at different levels of anesthesia. Increased propofol concentration correlated with decreased high-frequency power in LFP spectra and decreased AP firing rates, and the generation of large-amplitude spike-like LFP activity; however, the temporal relationship between APs and LFPs remained relatively consistent at all levels of propofol. The probability that an AP would fire at this local minimum of the LFP increased with propofol administration. The propofol-induced suppression of neocortical network activity allowed LFPs to be dominated by low-frequency spike-like activity, and correlated with sedation and unconsciousness. As the low-frequency spike-like activity increased and the AP-LFP relationship became more predictable firing rate encoding capacity is impaired. This suggests a mechanism for decreased information processing in the neocortex that accounts for propofol-induced unconsciousness.
Keywords: consciousness; local field potential; microelectrode array; power spectrum; propofol.
Figures
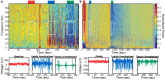
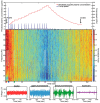
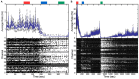
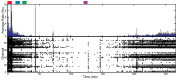
Similar articles
-
Relationships between spike-free local field potentials and spike timing in human temporal cortex.J Neurophysiol. 2012 Apr;107(7):1808-21. doi: 10.1152/jn.00663.2011. Epub 2011 Dec 7. J Neurophysiol. 2012. PMID: 22157112 Free PMC article.
-
Propofol Anesthesia Precludes LFP-Based Functional Mapping of Pallidum during DBS Implantation.Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2018;96(4):249-258. doi: 10.1159/000492231. Epub 2018 Sep 7. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 30196280 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of Propofol-Induced Loss of Consciousness Across Primate Neocortex.J Neurosci. 2016 Jul 20;36(29):7718-26. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4577-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27445148 Free PMC article.
-
Synchrony between single-unit activity and local field potentials in relation to periodicity coding in primary auditory cortex.J Neurophysiol. 1995 Jan;73(1):227-45. doi: 10.1152/jn.1995.73.1.227. J Neurophysiol. 1995. PMID: 7714568
-
Primary sensorimotor cortex exhibits complex dependencies of spike-field coherence on neuronal firing rates, field power, and behavior.J Neurophysiol. 2018 Jul 1;120(1):226-238. doi: 10.1152/jn.00037.2018. Epub 2018 Mar 28. J Neurophysiol. 2018. PMID: 29589815 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Low-Dimensional Models of "Neuro-Glio-Vascular Unit" for Describing Neural Dynamics under Normal and Energy-Starved Conditions.Front Neurol. 2016 Mar 9;7:24. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2016.00024. eCollection 2016. Front Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27014179 Free PMC article.
-
Propofol-induced Changes in α-β Sensorimotor Cortical Connectivity.Anesthesiology. 2018 Feb;128(2):305-316. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000001940. Anesthesiology. 2018. PMID: 29068830 Free PMC article.
-
Protocol for detecting and analyzing non-oscillatory traveling waves from high-spatiotemporal-resolution human electrophysiological recordings.STAR Protoc. 2025 Mar 21;6(1):103659. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2025.103659. Epub 2025 Feb 27. STAR Protoc. 2025. PMID: 40022738 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Fast Nerve Conduction Produced by Analgesics and Analgesic Adjuvants-Possible Involvement in Pain Alleviation.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020 Apr 5;13(4):62. doi: 10.3390/ph13040062. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32260535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Globus pallidus externus drives increase in network-wide alpha power with propofol-induced loss-of-consciousness in humans.Cereb Cortex. 2024 Jun 4;34(6):bhae243. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhae243. Cereb Cortex. 2024. PMID: 38850214 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bester L. (2009). Pharmacokinetics of Propofol in Cats. Ph.D. thesis, Master’s in Veterinary Medicine, University of Pretoria, Pretoria
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

