Eosinophil-expressed galectin-3 regulates cell trafficking and migration
- PMID: 23576987
- PMCID: PMC3617360
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2013.00037
Eosinophil-expressed galectin-3 regulates cell trafficking and migration
Abstract
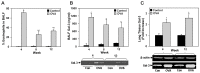
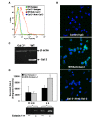
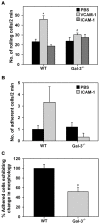
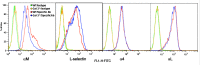
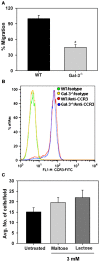
Galectin-3 (Gal-3), a β galactoside-binding lectin, is implicated in the pathogenesis of allergic airway inflammation and allergen-challenged mice deficient in Gal-3 (Gal-3(-/-)) exhibit decreased airway recruitment of eosinophils (Eos). Gal-3 is expressed and secreted by several cell types and can thus function extracellularly and intracellularly to regulate a variety of cellular responses. We sought to determine the role of Eos-expressed Gal-3 in promoting Eos trafficking and migration in the context of allergic airway inflammation using bone marrow (BM)-derived Eos from wild-type (WT) and Gal-3(-/-) mice. Airway recruitment of Eos in acute (4 weeks) and chronic (8-12 weeks) allergen-challenged WT mice correlated with Gal-3 expression in the lungs. BM-derived Eos were found to express Gal-3 on the cell surface and secrete soluble Gal-3 when exposed to eotaxin-1. Compared to WT Eos, Gal-3(-/-) Eos exhibited significantly reduced rolling on vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) and decreased stable adhesion on intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) under conditions of flow in vitro. Evaluation of cytoskeletal rearrangement demonstrated that relatively fewer adherent Gal-3(-/-) Eos undergo cell spreading and formation of membrane protrusions. In addition, cell surface expression of integrin receptor αM (CD11b) was lower in Gal-3(-/-) Eos, which is likely to account for their altered adhesive interactions with VCAM-1 and ICAM-1. Gal-3(-/-) Eos also exhibited significantly decreased migration toward eotaxin-1 compared to WT Eos irrespective of similar levels of CCR3 expression. Further, eotaxin-induced migration of WT Eos remained unaffected in the presence of lactose, suggesting a role for intracellular Gal-3 in regulating Eos migration. Overall, our findings indicate that Gal-3 expression in the lungs correlates with Eos mobilization during allergic airway inflammation and signaling involving intracellular Gal-3 and/or secreted Gal-3 bound to the cell surface of Eos appears to be essential for Eos trafficking under flow as well as for migration.
Keywords: allergic airway inflammation; cell trafficking; eosinophils; galectin-3; migration.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of eosinophilia and allergic airway inflammation by the glycan-binding protein galectin-1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Aug 16;113(33):E4837-46. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1601958113. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27457925 Free PMC article.
-
The p110δ subunit of PI3K regulates bone marrow-derived eosinophil trafficking and airway eosinophilia in allergen-challenged mice.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012 Jun 1;302(11):L1179-91. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00005.2012. Epub 2012 Mar 16. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22427531 Free PMC article.
-
Galectin-3 functions as an adhesion molecule to support eosinophil rolling and adhesion under conditions of flow.J Immunol. 2007 Dec 1;179(11):7800-7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.11.7800. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 18025226
-
Regulation of Eosinophil Recruitment and Activation by Galectins in Allergic Asthma.Front Med (Lausanne). 2017 May 31;4:68. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2017.00068. eCollection 2017. Front Med (Lausanne). 2017. PMID: 28620605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory mechanisms of eosinophil adhesion to and transmigration across endothelial cells by alpha4 and beta2 integrins.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1999;120 Suppl 1:24-6. doi: 10.1159/000053588. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10529598 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase, nitrotyrosine, eosinophilic peroxidase, eotaxin-3, and galectin-3 in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease, eosinophilic esophagitis, and in healthy controls: a semiquantitative image analysis of 3,3'-diaminobenzidine-stained esophageal biopsies.Dis Esophagus. 2024 Aug 29;37(9):doae034. doi: 10.1093/dote/doae034. Dis Esophagus. 2024. PMID: 38679488 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic determinants of circulating galectin-3 levels in patients with coronary artery disease.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020 Sep;8(9):e1370. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1370. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020. PMID: 32573962 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of eosinophilia and allergic airway inflammation by the glycan-binding protein galectin-1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Aug 16;113(33):E4837-46. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1601958113. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27457925 Free PMC article.
-
Galectin-3-Mediated Glial Crosstalk Drives Oligodendrocyte Differentiation and (Re)myelination.Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 Sep 12;12:297. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00297. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30258354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Galectin-3: A Positive Regulator of Leukocyte Recruitment in the Inflamed Microcirculation.J Immunol. 2017 Jun 1;198(11):4458-4469. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600709. Epub 2017 Apr 24. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28438899 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Broide D., Sriramarao P. (2008). “Cellular adhesion in inflammation” in Middleton’s Allergy Principles and Practice, Vol. 1 eds. Adkinson N. F., Holgate S. T., Busse W. W., Bochner B. S., Lemanske R. F., Jr., Adkinson N. F., Jr., et al.(Amsterdam: Mosby; ) 149–165
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

