Genome-scale screening of drug-target associations relevant to Ki using a chemogenomics approach
- PMID: 23577055
- PMCID: PMC3618265
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057680
Genome-scale screening of drug-target associations relevant to Ki using a chemogenomics approach
Abstract
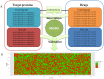
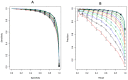
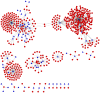
The identification of interactions between drugs and target proteins plays a key role in genomic drug discovery. In the present study, the quantitative binding affinities of drug-target pairs are differentiated as a measurement to define whether a drug interacts with a protein or not, and then a chemogenomics framework using an unbiased set of general integrated features and random forest (RF) is employed to construct a predictive model which can accurately classify drug-target pairs. The predictability of the model is further investigated and validated by several independent validation sets. The built model is used to predict drug-target associations, some of which were confirmed by comparing experimental data from public biological resources. A drug-target interaction network with high confidence drug-target pairs was also reconstructed. This network provides further insight for the action of drugs and targets. Finally, a web-based server called PreDPI-Ki was developed to predict drug-target interactions for drug discovery. In addition to providing a high-confidence list of drug-target associations for subsequent experimental investigation guidance, these results also contribute to the understanding of drug-target interactions. We can also see that quantitative information of drug-target associations could greatly promote the development of more accurate models. The PreDPI-Ki server is freely available via: http://sdd.whu.edu.cn/dpiki.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Large-scale prediction of human kinase-inhibitor interactions using protein sequences and molecular topological structures.Anal Chim Acta. 2013 Aug 20;792:10-8. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2013.07.003. Epub 2013 Jul 10. Anal Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23910962
-
TargetNet: a web service for predicting potential drug-target interaction profiling via multi-target SAR models.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2016 May;30(5):413-24. doi: 10.1007/s10822-016-9915-2. Epub 2016 May 11. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2016. PMID: 27167132
-
NL MIND-BEST: a web server for ligands and proteins discovery--theoretic-experimental study of proteins of Giardia lamblia and new compounds active against Plasmodium falciparum.J Theor Biol. 2011 May 7;276(1):229-49. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2011.01.010. Epub 2011 Jan 26. J Theor Biol. 2011. PMID: 21277861
-
Chemogenomics: bridging a drug discovery gap.Curr Med Chem. 2002 Dec;9(23):2077-84. doi: 10.2174/0929867023368728. Curr Med Chem. 2002. PMID: 12470247 Review.
-
Functional cell-based uHTS in chemical genomic drug discovery.Trends Biotechnol. 2002 Mar;20(3):110-5. doi: 10.1016/s0167-7799(02)01906-6. Trends Biotechnol. 2002. PMID: 11841862 Review.
Cited by
-
Predicting target-ligand interactions using protein ligand-binding site and ligand substructures.BMC Syst Biol. 2015;9 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S2. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-9-S1-S2. Epub 2015 Jan 21. BMC Syst Biol. 2015. PMID: 25707321 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical trials puzzle: How network effects limit drug discovery.iScience. 2023 Oct 30;26(12):108361. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108361. eCollection 2023 Dec 15. iScience. 2023. PMID: 38146432 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning approaches and databases for prediction of drug-target interaction: a survey paper.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Jan 18;22(1):247-269. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbz157. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 31950972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In-silico target prediction by ensemble chemogenomic model based on multi-scale information of chemical structures and protein sequences.J Cheminform. 2023 Apr 23;15(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s13321-023-00720-0. J Cheminform. 2023. PMID: 37088813 Free PMC article.
-
In silico methods for drug repurposing and pharmacology.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2016 May;8(3):186-210. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.1337. Epub 2016 Apr 15. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 27080087 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kuhn M, Campillos M, Gonzolez P, Jensen LJ, Bork P (2008) Large-scale prediction of drug-target relationships. FEBS letters 582: 1283–1290. - PubMed
-
- Yildirim MA, Goh KI, Cusick ME, Barabsi AL, Vidal M (2007) Drug-target network. Nat Biotechnol 25: 1119–1126. - PubMed
-
- Paolini GV, Shapland RHB, van Hoorn WP, Mason JS, Hopkins AL (2006) Global mapping of pharmacological space. Nat Biotech 24: 805–815. - PubMed
-
- Ashburn TT, Thor KB (2004) Drug repositioning: identifying and developing new uses for existing drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3: 673–683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

