Bacterial population in intestines of the black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) under different growth stages
- PMID: 23577162
- PMCID: PMC3618293
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060802
Bacterial population in intestines of the black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) under different growth stages
Abstract
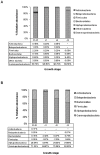
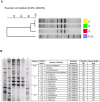
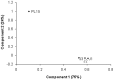
Intestinal bacterial communities in aquaculture have been drawn to attention due to potential benefit to their hosts. To identify core intestinal bacteria in the black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon), bacterial populations of disease-free shrimp were characterized from intestines of four developmental stages (15-day-old post larvae (PL15), 1- (J1), 2- (J2), and 3-month-old (J3) juveniles) using pyrosequencing, real-time PCR and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) approaches. A total of 25,121 pyrosequencing reads (reading length = 442±24 bases) were obtained, which were categorized by barcode for PL15 (7,045 sequences), J1 (3,055 sequences), J2 (13,130 sequences) and J3 (1,890 sequences). Bacteria in the phyla Bacteroides, Firmicutes and Proteobacteria were found in intestines at all four growth stages. There were 88, 14, 27, and 20 bacterial genera associated with the intestinal tract of PL15, J1, J2 and J3, respectively. Pyrosequencing analysis revealed that Proteobacteria (class Gammaproteobacteria) was a dominant bacteria group with a relative abundance of 89% for PL15 and 99% for J1, J2 and J3. Real-time PCR assay also confirmed that Gammaproteobacteria had the highest relative abundance in intestines from all growth stages. Intestinal bacterial communities from the three juvenile stages were more similar to each other than that of the PL shrimp based on PCA analyses of pyrosequencing results and their DGGE profiles. This study provides descriptive bacterial communities associated to the black tiger shrimp intestines during these growth development stages in rearing facilities.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Bacterial community associated with the intestinal tract of P. monodon in commercial farms.Microb Ecol. 2012 May;63(4):938-53. doi: 10.1007/s00248-011-9936-2. Epub 2011 Sep 14. Microb Ecol. 2012. PMID: 21915632
-
Characterization of intestinal bacteria in wild and domesticated adult black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon).PLoS One. 2014 Mar 11;9(3):e91853. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091853. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24618668 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial dynamics in intestines of the black tiger shrimp and the Pacific white shrimp during Vibrio harveyi exposure.J Invertebr Pathol. 2016 Jan;133:12-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2015.11.004. Epub 2015 Nov 14. J Invertebr Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26585302
-
Bacterial analysis in the early developmental stages of the black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon).Sci Rep. 2020 Mar 17;10(1):4896. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-61559-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32184459 Free PMC article.
-
Advances, challenges, and directions in shrimp disease control: the guidelines from an ecological perspective.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016 Aug;100(16):6947-54. doi: 10.1007/s00253-016-7679-1. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27333908 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessing interactions, predicting function, and increasing degradation potential of a PAH-degrading bacterial consortium by effect of an inoculant strain.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Sep;26(25):25932-25944. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05760-4. Epub 2019 Jul 4. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31273663
-
Intestinal Microbiota of White Shrimp Penaeus vannamei Under Intensive Cultivation Conditions in Ecuador.Microb Ecol. 2018 Apr;75(3):562-568. doi: 10.1007/s00248-017-1066-z. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Microb Ecol. 2018. PMID: 28929202
-
Comparison of the Intestinal Microbiota During the Different Growth Stages of Red Swamp Crayfish (Procambarus clarkii).Front Microbiol. 2021 Sep 13;12:696281. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.696281. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34589066 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial Community Associated with Healthy and Diseased Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Larvae and Rearing Water across Different Growth Stages.Front Microbiol. 2017 Jul 18;8:1362. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01362. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28769916 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of dietary poly-β-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) on microbiota composition and the mTOR signaling pathway in the intestines of litopenaeus vannamei.J Microbiol. 2017 Dec;55(12):946-954. doi: 10.1007/s12275-017-7273-y. Epub 2017 Dec 7. J Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29214487
References
-
- Hooper LV, Midtvedt T, Gordon JI (2002) How host-microbial interactions shape the nutrient environment of the mammalian intestine. Annu Rev Nutr 22: 283–307. - PubMed
-
- Brune A, Friedrich M (2000) Microecology of the termite gut: structure and function on a microscale. Curr Opin Microbiol 3: 263–269. - PubMed
-
- Harris JM (1993) The presence, nature, and role of gut microflora in aquatic invertebrates: A synthesis. Microbial Ecol 25: 195–231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

