Methylation of mercury in earthworms and the effect of mercury on the associated bacterial communities
- PMID: 23577209
- PMCID: PMC3618111
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061215
Methylation of mercury in earthworms and the effect of mercury on the associated bacterial communities
Abstract
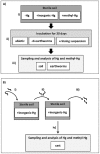
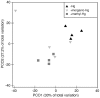
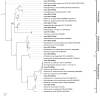
Methylmercury compounds are very toxic for most organisms. Here, we investigated the potential of earthworms to methylate inorganic-Hg. We hypothesized that the anaerobic and nutrient-rich conditions in the digestive tracts of earthworm's promote the methylation of Hg through the action of their gut bacteria. Earthworms were either grown in sterile soils treated with an inorganic (HgCl2) or organic (CH3HgCl) Hg source, or were left untreated. After 30 days of incubation, the total-Hg and methyl-Hg concentrations in the soils, earthworms, and their casts were analyzed. The impact of Hg on the bacterial community compositions in earthworms was also studied. Tissue concentrations of methyl-Hg in earthworms grown in soils treated with inorganic-Hg were about six times higher than in earthworms grown in soils without Hg. Concentrations of methyl-Hg in the soils and earthworm casts remained at significantly lower levels suggesting that Hg was mainly methylated in the earthworms. Bacterial communities in earthworms were mostly affected by methyl-Hg treatment. Terminal-restriction fragments (T-RFs) affiliated to Firmicutes were sensitive to inorganic and methyl-Hg, whereas T-RFs related to Betaproteobacteria were tolerant to the Hg treatments. Sulphate-reducing bacteria were detected in earthworms but not in soils.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Using species-specific enriched stable isotopes to study the effect of fresh mercury inputs in soil-earthworm systems.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2018 Jan;147:192-199. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.08.015. Epub 2017 Sep 14. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2018. PMID: 28843190
-
Accumulation of mercury and methylmercury by mushrooms and earthworms from forest soils.Environ Pollut. 2011 Oct;159(10):2861-9. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2011.04.040. Epub 2011 May 28. Environ Pollut. 2011. PMID: 21621314
-
Total mercury and methylmercury concentrations over a gradient of contamination in earthworms living in rice paddy soil.Environ Toxicol Chem. 2017 May;36(5):1202-1210. doi: 10.1002/etc.3643. Epub 2016 Nov 11. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2017. PMID: 27699848
-
Mercury methylation in rice paddy and accumulation in rice plant: A review.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2020 Jun 1;195:110462. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110462. Epub 2020 Mar 13. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2020. PMID: 32179234 Review.
-
Modeling Mercury in Proteins.Methods Enzymol. 2016;578:103-22. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2016.05.041. Epub 2016 Jul 1. Methods Enzymol. 2016. PMID: 27497164 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Mercury Contamination on Microbial Diversity of Different Kinds of Soil.Microorganisms. 2022 May 7;10(5):977. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10050977. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35630421 Free PMC article.
-
Bioaccumulation of methylmercury within the marine food web of the outer Bay of Fundy, Gulf of Maine.PLoS One. 2018 Jul 16;13(7):e0197220. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197220. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30011281 Free PMC article.
-
Short-term Effects of Cadmium and Mercury on Soil Nematode Communities in a Pot Experiment.Helminthologia. 2020 May 23;57(2):145-153. doi: 10.2478/helm-2020-0015. eCollection 2020 Jun 1. Helminthologia. 2020. PMID: 32518490 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress, Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity in Earthworm Eisenia fetida at Different Di-n-Butyl Phthalate Exposure Levels.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 16;11(3):e0151128. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151128. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26982081 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schroeder WH, Munthe J (1998) Atmospheric mercury-An overview. Atmos Environ 32: 809–822.
-
- Swain EB, Jakus PM, Rice G, Lupi F, Maxson PA, et al. (2007) Socioeconomic consequences of mercury use and pollution. Ambio 36: 45–61. - PubMed
-
- Skyllberg U, Drott A (2010) Competition between disordered iron sulfide and natural organic matter associated thiols for mercury(II)-an EXAFS study. Environ Sci Technol 44: 1254–1259. - PubMed
-
- Tipping E, Lofts S, Hooper H, Frey B, Spurgeon D, et al. (2010) Critical Limits for Hg(II) in soils, derived from chronic toxicity data. Environ Pollut 158: 2465–2471. - PubMed
-
- Rieder SR, Brunner I, Horvat M, Jacobs A, Frey B (2011) Accumulation of mercury and methylmercury by mushrooms and earthworms from forest soils. Environ Pollut 159: 2861–2869. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

