Field evaluation of HRP2 and pan pLDH-based immunochromatographic assay in therapeutic monitoring of uncomplicated falciparum malaria in Myanmar
- PMID: 23577630
- PMCID: PMC3636062
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2875-12-123
Field evaluation of HRP2 and pan pLDH-based immunochromatographic assay in therapeutic monitoring of uncomplicated falciparum malaria in Myanmar
Abstract
Background: Malaria rapid diagnostic tests (RDT) are used for diagnostic purpose in malaria-endemic areas where reliable microscopy is not available. Persistence of the antigenaemia causes over-diagnosis and may limit the usefulness of the RDT in monitoring treatment. In this study, the usefulness of histidine-rich protein-2 (HRP2) and pan-specific or species-specific Plasmodium lactate dehydrogenase (pLDH) in treatment monitoring of uncomplicated falciparum malaria was carried out in an endemic setting in Myanmar.
Methods: A prospective longitudinal, single-arm, cohort study was done by microscopy to confirm Plasmodium falciparum mono-infected cases. After direct treatment with an artemether-lumefantrine combination, patients were followed up on day 3, 7, 14, 21, 28 and any other day of recurrent fever. Blood film examination and RDT were carried out on day 0 and all follow-up days.
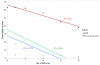
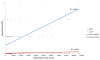
Results: Out of 77 recruited falciparum cases, 63 became adequate clinical and parasitological response (ACPR) cases, and 60.3% of them were still positive for HRP2 up to day 28. Eleven out of 12 treatment failure cases (91.6%) were detected by pan pLDH. The mean duration required to become negative of HRP2 was 20 days (SD ± 6.03) and that of pan pLDH was six days with or without gametocytes and 3.7 days without gametocytes.
Conclusion: Although treatment monitoring cannot be performed by HRP2, it can be assessed by pan pLDH-based assay after day 3 if a gametocidal drug has been administered and after day 7 if the presence of gametocytes was not excluded. The pan pLDH-based assay was a suitable test to monitor the treatment response of uncomplicated falciparum malaria patients.
Figures
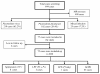
References
-
- WHO. Methods for surveillance of antimalarial drug efficacy. Global malaria programme. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2009.
-
- Leke RFG, Djokam RR, Mbu R, Leke RJ, Fogako J, Megnekou R, Metenou S, Sama G, Zhou Y, Cadigan T, Parra M, Taylor W. Detection of the Plasmodium falciparum antigen histidine-rich protein 2 in blood of pregnant women: implications for diagnosing placental malaria. J Clin Microbiol. 1999;37:2992–2996. - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO. New perspective: malaria diagnosis. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2000.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

