Intrauterine growth restriction and congenital malformations: a retrospective epidemiological study
- PMID: 23578323
- PMCID: PMC3639199
- DOI: 10.1186/1824-7288-39-23
Intrauterine growth restriction and congenital malformations: a retrospective epidemiological study
Abstract
Background: Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) and small for gestational age (SGA) birth have been considered possible indicators of the presence of malformations. The aim of this study is to evaluate such relationships in a population of newborns, along with other epidemiological and auxological parameters, in particular the ponderal index (PI).
Methods: We analyzed the birth data of 1093 infants, classified according to weight for gestational age as SGA, appropriate for gestational age (AGA) or large for gestational age (LGA). The prevalence of malformations was analyzed in relation to weight percentile at birth and SGA birth, maternal smoking, pregnancy diseases and PI.
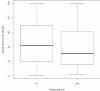
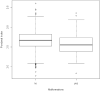
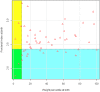
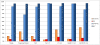
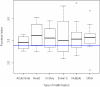
Results: Our analysis showed no significant relationship between the prevalence of malformations and SGA birth. Maternal smoking and pregnancy diseases were strongly related to SGA birth, but not to a higher prevalence of malformations. PI, however, had a significant relationship with a higher prevalence of malformations, if analyzed as either a continuous variable or a categorical variable (cutoff: < 2.4).
Conclusions: The association between congenital malformations and birth weight for gestational age seems to be weak. As part of diagnostic screening for malformations in the neonatal period, PI could be considered a better predictor of risk than weight percentile.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intrauterine growth pattern and birthweight discordance in twin pregnancies: a retrospective study.Ital J Pediatr. 2014 May 5;40:43. doi: 10.1186/1824-7288-40-43. Ital J Pediatr. 2014. PMID: 24887062 Free PMC article.
-
Mortality and morbidity in infants with intrauterine growth retardation.J Pediatr. 1982 Dec;101(6):978-83. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80025-5. J Pediatr. 1982. PMID: 6890576
-
Prediction factors in the determination of final height in subjects born small for gestational age.Pediatr Res. 1998 Jun;43(6):808-12. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199806000-00015. Pediatr Res. 1998. PMID: 9621992
-
Undernutrition and growth restriction in pregnancy.Nestle Nutr Workshop Ser Pediatr Program. 2008;61:103-21. doi: 10.1159/000113181. Nestle Nutr Workshop Ser Pediatr Program. 2008. PMID: 18196948 Review.
-
[Prevalence, risk factors, maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality of intrauterine growth restriction and small-for-gestational age].J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2013 Dec;42(8):895-910. doi: 10.1016/j.jgyn.2013.09.013. Epub 2013 Nov 9. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2013. PMID: 24216305 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Growth and risk of adverse neurodevelopmental outcome in infants with congenital surgical anomalies: a systematic review.Pediatr Surg Int. 2022 Nov 28;39(1):3. doi: 10.1007/s00383-022-05305-w. Pediatr Surg Int. 2022. PMID: 36441273
-
Intrauterine growth pattern and birthweight discordance in twin pregnancies: a retrospective study.Ital J Pediatr. 2014 May 5;40:43. doi: 10.1186/1824-7288-40-43. Ital J Pediatr. 2014. PMID: 24887062 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiological and Histopathological Characteristics of Fetuses with Congenital Disorders: A Study in Greece.Biology (Basel). 2025 May 29;14(6):626. doi: 10.3390/biology14060626. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40563877 Free PMC article.
-
Postnatal Growth in a Cohort of Sardinian Intrauterine Growth-Restricted Infants.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:9382083. doi: 10.1155/2017/9382083. Epub 2017 Jun 20. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28713832 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review and quantitative assessment of sleep-disordered breathing during pregnancy and perinatal outcomes.Sleep Breath. 2014 Dec;18(4):703-13. doi: 10.1007/s11325-014-0946-4. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Sleep Breath. 2014. PMID: 24519711
References
-
- Corsello G, Giuffrè M. Congenital malformations. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012;25(Suppl 1):25–29. - PubMed
-
- Giuffrè M, Piro E, Corsello G. Prematurity and twinning. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012;25(Suppl 3):6–10. - PubMed
-
- Lituania M, Passamonti U, Esposito V. Genetic factors and fetal anomalies in intrauterine growth retardation. Journ Perinat Med. 1994;22(Suppl.1):79–83. - PubMed
-
- Khoury MJ, Erickson JD, Corsero JF, McCarthy BJ. Congenital malformations and intrauterine growth retardation: a population study. Pediatrics. 1988;82:83–90. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

