SULT2B1b sulfotransferase: induction by vitamin D receptor and reduced expression in prostate cancer
- PMID: 23579488
- PMCID: PMC3656233
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2012-1369
SULT2B1b sulfotransferase: induction by vitamin D receptor and reduced expression in prostate cancer
Abstract
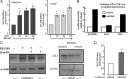
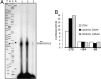
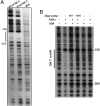
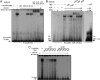
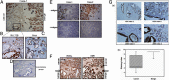
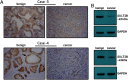
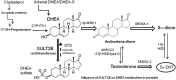
An elevated tumor tissue androgen level, which reactivates androgen receptor in recurrent prostate cancer, arises from the intratumor synthesis of 5α-dihydrotestosterone through use of the precursor steroid dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and is fueled by the steroidogenic enzymes 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3β-HSD1), aldoketoreductase (AKR1C3), and steroid 5-alpha reductase, type 1 (SRD5A1) present in cancer tissue. Sulfotransferase 2B1b (SULT2B1b) (in short, SULT2B) is a prostate-expressed hydroxysteroid SULT that converts cholesterol, oxysterols, and DHEA to 3β-sulfates. DHEA metabolism involving sulfonation by SULT2B can potentially interfere with intraprostate androgen synthesis due to reduction of free DHEA pool and, thus, conversion of DHEA to androstenedione. Here we report that in prostatectomy specimens from treatment-naive patients, SULT2B expression is markedly reduced in malignant tissue (P < .001, Mann-Whitney U test) compared with robust expression in adjacent nonmalignant glands. SULT2B was detected in formalin-fixed specimens by immunohistochemistry on individual sections and tissue array. Immunoblotting of protein lysates of frozen cancer and matched benign tissue confirmed immunohistochemistry results. An in-house-developed rabbit polyclonal antibody against full-length human SULT2B was validated for specificity and used in the analyses. Ligand-activated vitamin D receptor induced the SULT2B1 promoter in vivo in mouse prostate and increased SULT2B mRNA and protein levels in vitro in prostate cancer cells. A vitamin D receptor/retinoid X receptor-α-bound DNA element (with a DR7 motif) mediated induction of the transfected SULT2B1 promoter in calcitriol-treated cells. SULT2B knockdown caused an increased proliferation rate of prostate cancer cells upon stimulation by DHEA. These results suggest that the tumor tissue SULT2B level may partly control prostate cancer growth, and its induction in a therapeutic setting may inhibit disease progression.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibitory Interplay of SULT2B1b Sulfotransferase with AKR1C3 Aldo-keto Reductase in Prostate Cancer.Endocrinology. 2020 Feb 1;161(2):bqz042. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqz042. Endocrinology. 2020. PMID: 31894239 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of SULT2B1b expression alters effects of 3beta-hydroxysteroids on cell proliferation and steroid hormone receptor expression in human LNCaP prostate cancer cells.Prostate. 2007 Sep 1;67(12):1318-29. doi: 10.1002/pros.20615. Prostate. 2007. PMID: 17626250
-
Upregulation of hydroxysteroid sulfotransferase 2B1b promotes hepatic oval cell proliferation by modulating oxysterol-induced LXR activation in a mouse model of liver injury.Arch Toxicol. 2017 Jan;91(1):271-287. doi: 10.1007/s00204-016-1693-z. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Arch Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27052460
-
Vitamin D in Prostate Cancer.Vitam Horm. 2016;100:321-55. doi: 10.1016/bs.vh.2015.10.012. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Vitam Horm. 2016. PMID: 26827958 Review.
-
SULT2B1: unique properties and characteristics of a hydroxysteroid sulfotransferase family.Drug Metab Rev. 2013 Nov;45(4):388-400. doi: 10.3109/03602532.2013.835609. Epub 2013 Sep 10. Drug Metab Rev. 2013. PMID: 24020383 Review.
Cited by
-
The Important Roles of Steroid Sulfatase and Sulfotransferases in Gynecological Diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2016 Feb 18;7:30. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00030. eCollection 2016. Front Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26924986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relationships between hyperinsulinaemia, magnesium, vitamin D, thrombosis and COVID-19: rationale for clinical management.Open Heart. 2020 Sep;7(2):e001356. doi: 10.1136/openhrt-2020-001356. Open Heart. 2020. PMID: 32938758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human sulfotransferase SULT2B1 physiological role and the impact of genetic polymorphism on enzyme activity and pathological conditions.Front Genet. 2024 Aug 30;15:1464243. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1464243. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 39280099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct expression patterns of SULT2B1b in human prostate epithelium.Prostate. 2019 Aug;79(11):1256-1266. doi: 10.1002/pros.23829. Epub 2019 Jun 18. Prostate. 2019. PMID: 31212370 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D in prostate cancer.Asian J Androl. 2018 May-Jun;20(3):244-252. doi: 10.4103/aja.aja_14_18. Asian J Androl. 2018. PMID: 29667615 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hofland J, van Weerden WM, Dits NF, et al. Evidence of Limited contributions for intratumoral steroidogenesis in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2010;70:1256–1264 - PubMed
-
- Hofland J, van Weerden WM, Jenster G, Schröder FH, de Jong FH. Intraprostatic steroidogenic enzymes: response. Cancer Res. 2010;70:8249–8250
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

