The role of leptin in the control of insulin-glucose axis
- PMID: 23579596
- PMCID: PMC3619125
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2013.00051
The role of leptin in the control of insulin-glucose axis
Abstract
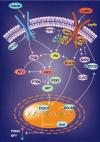
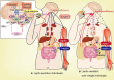
Obesity and diabetes mellitus are great public health concerns throughout the world because of their increasing incidence and prevalence. Leptin, the adipocyte hormone, is well known for its role in the regulation of food intake and energy expenditure. In addition to the regulation of appetite and satiety that recently has attracted much attentions, insight has also been gained into the critical role of leptin in the control of the insulin-glucose axis, peripheral glucose and insulin responsiveness. Since the discovery of leptin, leptin has been taken for its therapeutic potential to obesity and diabetes. Recently, the therapeutic effects of central leptin gene therapy have been reported in insulin-deficient diabetes in obesity animal models such as ob/ob mise, diet-induced obese mice, and insulin-deficient type 1 diabetes mice, and also in patients with inactivating mutations in the leptin gene. Herein, we review the role of leptin in regulating feeding behavior and glucose metabolism and also the therapeutic potential of leptin in obesity and diabetes mellitus.
Keywords: adipo-insulin axis; food intake; leptin; leptin gene therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Akiyama T., Tachibana I., Shirohara H., Watanabe N., Otsuki M. (1996). High-fat hypercaloric diet induces obesity, glucose intolerance and hyperlipidemia in normal adult male Wistar rat. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 31, 27–35 - PubMed
-
- Asakawa A., Inui A., Inui T., Katsuura G., Fujino M. A., Kasuga M. (2003). Leptin treatment ameliorates anxiety in ob/ob obese mice. J. Diabetes Complicat. 17, 105–107 - PubMed
-
- Asakawa A., Inui A., Ueno N., Makino S., Fujino M. A., Kasuga M. (1999). Urocortin reduces food intake and gastric emptying in lean and ob/ob obese mice. Gastroenterology 116, 1287–1292 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

