Focus on: neurotransmitter systems
- PMID: 23580048
- PMCID: PMC3860557
Focus on: neurotransmitter systems
Abstract
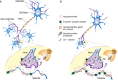
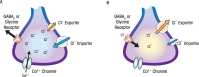
Neurotransmitter systems have been long recognized as important targets of the developmental actions of alcohol (i.e., ethanol). Short- and long-term effects of ethanol on amino acid (e.g., γ-aminobutyric acid and glutamate) and biogenic amine (e.g., serotonin and dopamine) neurotransmitters have been demonstrated in animal models of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASD). Researchers have detected ethanol effects after exposure during developmental periods equivalent to the first, second, and third trimesters of human pregnancy. Results support the recommendation that pregnant women should abstain from drinking-even small quantities-as effects of ethanol on neurotransmitter systems have been detected at low levels of exposure. Recent studies have elucidated new mechanisms and/or consequences of the actions of ethanol on amino acid and biogenic amine neuro-transmitter systems. Alterations in these neurotransmitter systems could, in part, be responsible for many of the conditions associated with FASD, including (1) learning, memory, and attention deficits; (2) motor coordination impairments; (3) abnormal responsiveness to stress; and (4) increased susceptibility to neuropsychiatric disorders, such as substance abuse and depression, and also neurological disorders, such as epilepsy and sudden infant death syndrome. However, future research is needed to conclusively establish a causal relationship between these conditions and developmental dysfunctions in neurotransmitter systems.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Does moderate drinking harm the fetal brain? Insights from animal models.Trends Neurosci. 2012 May;35(5):284-92. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2012.01.006. Epub 2012 Mar 6. Trends Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22402065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early Postnatal Ethanol Exposure in Mice Induces Sex-Dependent Memory Impairment and Reduction of Hippocampal NMDA-R2B Expression in Adulthood.Neuroscience. 2020 Feb 10;427:105-115. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.11.045. Epub 2019 Dec 23. Neuroscience. 2020. PMID: 31874240
-
A new method for quantifying prenatal exposure to ethanol by microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) of meconium followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS).Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012 Jul;404(1):147-55. doi: 10.1007/s00216-012-6108-2. Epub 2012 Jun 6. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012. PMID: 22669306
-
Quantifying fetal alcohol exposure by meconium fatty acid ethyl esters (FAEE); association with adverse fetal outcomes and population estimates of fetal alcohol exposure.Drug Metab Rev. 2019 Nov;51(4):524-532. doi: 10.1080/03602532.2019.1671859. Epub 2019 Oct 9. Drug Metab Rev. 2019. PMID: 31595802 Review.
-
Adequacy of maternal iron status protects against behavioral, neuroanatomical, and growth deficits in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47499. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047499. Epub 2012 Oct 19. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23094056 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Epigenetics of Anxiety Pathophysiology: A DNA Methylation and Histone Modification Focused Review.eNeuro. 2023 Apr 24;10(4):ENEURO.0109-21.2021. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0109-21.2021. Print 2023 Apr. eNeuro. 2023. PMID: 35998298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurological Disorders Induced by Drug Use: Effects of Adolescent and Embryonic Drug Exposure on Behavioral Neurodevelopment.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 30;25(15):8341. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158341. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Moderate Prenatal Alcohol Exposure Alters Functional Connectivity in the Adult Rat Brain.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016 Oct;40(10):2134-2146. doi: 10.1111/acer.13175. Epub 2016 Aug 29. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016. PMID: 27570053 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of alcohol exposure on neural development and network formation in human cortical organoids.Mol Psychiatry. 2023 Apr;28(4):1571-1584. doi: 10.1038/s41380-022-01862-7. Epub 2022 Nov 16. Mol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36385168 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic alcohol alters dendritic spine development in neurons in primary culture.Neurotox Res. 2013 Nov;24(4):532-48. doi: 10.1007/s12640-013-9409-0. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Neurotox Res. 2013. PMID: 23820986
References
-
- Alati R, Al Mamun A, Williams GM, et al. In utero alcohol exposure and prediction of alcohol disorders in early adulthood: A birth cohort study. Archives of General Psychiatry. 2006;63:1009–1016. - PubMed
-
- Baer JS, Sampson PD, Barr HM, et al. A 21-year longitudinal analysis of the effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on young adult drinking. Archives of General Psychiatry. 2003;60:377–385. - PubMed
-
- Bailey CD, Brien JF, Reynolds JN. Chronic prenatal ethanol exposure alters the proportion of GABAergic neurons in layers II/III of the adult guinea pig somatosensory cortex. Neurotoxicology and Teratology. 2004;26:59–63. - PubMed
-
- Barbier E, Houchi H, Warnault V, et al. Effects of prenatal and postnatal maternal ethanol on offspring response to alcohol and psychostimulants in Long Evans rats. Neuroscience. 2009;161:427–440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
