Inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase enhances the T-cell response to influenza virus infection
- PMID: 23580425
- PMCID: PMC3709631
- DOI: 10.1099/vir.0.053124-0
Inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase enhances the T-cell response to influenza virus infection
Abstract
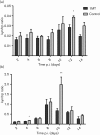
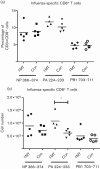
Influenza infection induces an increase in the level of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) activity in the lung parenchyma. IDO is the first and rate-limiting step in the kynurenine pathway where tryptophan is reduced to kynurenine and other metabolites. The depletion of tryptophan, and production of associated metabolites, attenuates the immune response to infection. The impact of IDO on the primary immune response to influenza virus infection was determined using the IDO inhibitor 1-methyl-D,L-tryptophan (1MT). C57BL/6 mice treated with 1MT and infected with A/HKx31 influenza virus had increased numbers of activated and functional CD4⁺ T-cells, influenza-specific CD8⁺ T-cells and effector memory cells in the lung. Inhibition of IDO increased the Th1 response in CD4⁺ T-cells as well as enhanced the Th17 response. These studies show that inhibition of IDO engenders a more robust T-cell response to influenza virus, and suggests an approach for enhancing the immune response to influenza vaccination by facilitating increased influenza-specific T-cell response.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) activity during the primary immune response to influenza infection modifies the memory T cell response to influenza challenge.Viral Immunol. 2014 Apr;27(3):112-23. doi: 10.1089/vim.2013.0105. Epub 2014 Apr 4. Viral Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24702331 Free PMC article.
-
Induction and role of indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase in mouse models of influenza a virus infection.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 13;8(6):e66546. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066546. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23785507 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of immunodominant antitumor and antiviral CD8+ T cell responses by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 28;9(2):e90439. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090439. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24587363 Free PMC article.
-
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-2; a new enzyme in the kynurenine pathway.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 Mar;41(3):467-71. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2008.01.005. Epub 2008 Jan 11. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 18282734 Review.
-
Tumor immune escape mediated by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase.Immunol Lett. 2007 Aug 15;111(2):69-75. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2007.06.001. Epub 2007 Jul 2. Immunol Lett. 2007. PMID: 17644189 Review.
Cited by
-
Tryptophan: A Unique Role in the Critically Ill.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 28;22(21):11714. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111714. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The immunotherapeutic role of regulatory T cells in Leishmania (Viannia) panamensis infection.J Immunol. 2014 Sep 15;193(6):2961-70. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1400728. Epub 2014 Aug 6. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25098291 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase reduces mortality from peritonitis and sepsis in mice by regulating functions of CD11b+ peritoneal cells.Infect Immun. 2014 Nov;82(11):4487-95. doi: 10.1128/IAI.02113-14. Epub 2014 Aug 11. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 25114116 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights into IDO Biology in Bacterial and Viral Infections.Front Immunol. 2014 Aug 11;5:384. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00384. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25157255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decreased IDO1-dependent tryptophan metabolism in aged lung during influenza.Eur Respir J. 2021 May 13;57(5):2000443. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00443-2020. Print 2021 May. Eur Respir J. 2021. PMID: 33243840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersson J., Boasso A., Nilsson J., Zhang R., Shire N. J., Lindback S., Shearer G. M., Chougnet C. A. (2005). The prevalence of regulatory T cells in lymphoid tissue is correlated with viral load in HIV-infected patients. J Immunol 174, 3143–3147 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

