Blockade of chronic type I interferon signaling to control persistent LCMV infection
- PMID: 23580528
- PMCID: PMC3704950
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1235208
Blockade of chronic type I interferon signaling to control persistent LCMV infection
Abstract
Type I interferons (IFN-I) are critical for antiviral immunity; however, chronic IFN-I signaling is associated with hyperimmune activation and disease progression in persistent infections. We demonstrated in mice that blockade of IFN-I signaling diminished chronic immune activation and immune suppression, restored lymphoid tissue architecture, and increased immune parameters associated with control of virus replication, ultimately facilitating clearance of the persistent infection. The accelerated control of persistent infection induced by blocking IFN-I signaling required CD4 T cells and was associated with enhanced IFN-γ production. Thus, we demonstrated that interfering with chronic IFN-I signaling during persistent infection redirects the immune environment to enable control of infection.
Figures
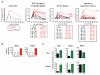
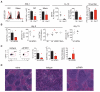

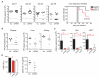
Comment in
-
Immunology. An interferon paradox.Science. 2013 Apr 12;340(6129):155-6. doi: 10.1126/science.1237568. Science. 2013. PMID: 23580520 Free PMC article.
-
Infection: the interferon paradox.Nat Rev Immunol. 2013 Jun;13(6):392. doi: 10.1038/nri3461. Epub 2013 May 7. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23648970 No abstract available.
-
Interfering with type I interferon: a novel approach to purge persistent viral infection.Cell Cycle. 2013 Sep 15;12(18):2919-20. doi: 10.4161/cc.26175. Epub 2013 Aug 23. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23974094 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- AI085043/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 8UL1TR000077-04/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI047868/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI085043/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL108949/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI056154/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AR063020/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI082975/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL108949/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI082975/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI060567/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI028697/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI060567/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000077/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

