Auxin biosynthesis and storage forms
- PMID: 23580748
- PMCID: PMC3695655
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/ert080
Auxin biosynthesis and storage forms
Abstract
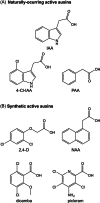
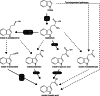
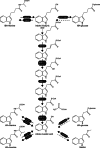
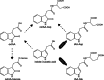
The plant hormone auxin drives plant growth and morphogenesis. The levels and distribution of the active auxin indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) are tightly controlled through synthesis, inactivation, and transport. Many auxin precursors and modified auxin forms, used to regulate auxin homeostasis, have been identified; however, very little is known about the integration of multiple auxin biosynthesis and inactivation pathways. This review discusses the many ways auxin levels are regulated through biosynthesis, storage forms, and inactivation, and the potential roles modified auxins play in regulating the bioactive pool of auxin to affect plant growth and development.
Keywords: IAA; IBA.; auxin; auxin biosynthesis; auxin conjugates; development.
Figures
References
-
- Abe H, Uchiyama M, Sato R. 1974. Isolation of phenylacetic acid and its p-hydroxy derivative as auxin-like substances from Undaria pinnatifida . Agricultural and Biological Chemistry 38, 897–898
-
- Aung LH. 1972. The nature of root-promoting substances in Lycopersicon esculentum seedlings. Physiologia Plantarum 26, 306–309
-
- Badenoch-Jones J, Summons RE, Rolfe BG, Letham DS. 1984. Phytohormones, Rhizobium mutants, and nodulation in legumes. IV. Auxin metabolites in pea root nodules. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation 3, 23–39
-
- Bajguz A, Piotrowska A. 2009. Conjugates of auxin and cytokinin. Phytochemistry 70, 957–969 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

