Ocular involvement of brucellosis
- PMID: 23580863
- PMCID: PMC3617540
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-9233.106407
Ocular involvement of brucellosis
Abstract
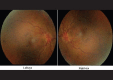
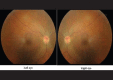
A 29-year-old male diagnosed with brucellosis a week earlier was referred to the ophthalmology clinic with visual complaints. On examination, visual acuity was 20/25, he had conjunctival injection on slit lamp examination. There was also bilateral optic disk swelling plus retinal hyperemia (optic disc hyperemia and vascular tortuosity) and intraretinal hemorrhage on funduscopy. The patient was admitted and treated with cotrimoxazole, rifampin, doxycycline and prednisolone for 2 months. Ocular manifestations subsided gradually within 6 months after treatment. Brucellosis can affect the eye and lead to serious ocular complications. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment should be considered in endemic areas.
Keywords: Bilateral optic disc swelling; Brucellosis; Ocular Brucellosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bilateral severe visual loss in brucellosis.Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2004 Sep;12(3):233-6. doi: 10.1080/092739490500183. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2004. PMID: 15385199
-
Ocular involvement in brucellosis.Can J Ophthalmol. 2009 Oct;44(5):598-601. doi: 10.3129/i09-019. Can J Ophthalmol. 2009. PMID: 19789599
-
Brucella meningitis and papilledema in a child.Eur J Ophthalmol. 2005 Nov-Dec;15(6):818-20. doi: 10.1177/112067210501500628. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2005. PMID: 16329074
-
Bilateral optic papillitis following mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia.Ophthalmologica. 1998;212(5):344-6. doi: 10.1159/000027322. Ophthalmologica. 1998. PMID: 9693295 Review.
-
Bilateral multifocal choroiditis with serous retinal detachment in a patient with Brucella infection: case report and review of the literature.Arch Ophthalmol. 2005 Jan;123(1):116-8. doi: 10.1001/archopht.123.1.116. Arch Ophthalmol. 2005. PMID: 15642826 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Infectious eye disease in the 21st century-an overview.Eye (Lond). 2024 Aug;38(11):2014-2027. doi: 10.1038/s41433-024-02966-w. Epub 2024 Feb 14. Eye (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38355671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brucellosis: epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment-a comprehensive review.Ann Med. 2023;55(2):2295398. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2295398. Epub 2024 Jan 2. Ann Med. 2023. PMID: 38165919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recurrent Fevers and Neuro-ophthalmic Disorders in a Mathematical Genius.Neuroophthalmology. 2021 Mar 1;45(2):131-138. doi: 10.1080/01658107.2020.1835993. eCollection 2021. Neuroophthalmology. 2021. PMID: 34108785 Free PMC article.
-
Fulminant endogenous endophthalmitis caused by Brucella melitensis, a case report.Clin Case Rep. 2023 Nov 13;11(11):e8200. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.8200. eCollection 2023 Nov. Clin Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 38028096 Free PMC article.
-
Comparisons of brucellosis between human and veterinary medicine.Infect Ecol Epidemiol. 2018 Jul 24;8(1):1500846. doi: 10.1080/20008686.2018.1500846. eCollection 2018. Infect Ecol Epidemiol. 2018. PMID: 30083304 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Young EJ. Brucella species. In: Mandle GI, Bennett JE, editors. Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. New York: Churchill Livingstone Inc; 2010. pp. 2921–25.
-
- Hall WH. Brucellosis. In: Evans AS, Brachman PS, editors. Bacterial Infections in Humans. New York: Plenum Publishing Crop; 1991. pp. 133–149.
-
- Doganay M, Aygen B. Human brucellosis: an overview. Int J Infect Dis. 2003;7:173–82.
-
- Sauret JM, Vilissova N. Human brucellosis. J Am Board Fam Pract. 2002;15:401–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources