Role of diacylglycerol kinases in T cell development and function
- PMID: 23582058
- PMCID: PMC3689416
- DOI: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.2013006696
Role of diacylglycerol kinases in T cell development and function
Abstract
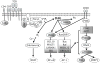
Diacylglycerol (DAG), a second messenger generated by phospholipase Cγ1 activity upon engagement of a T-cell receptor, triggers several signaling cascades that play important roles in T cell development and function. A family of enzymes called DAG kinases (DGKs) catalyzes the phosphorylation of DAG to phosphatidic acid, acting as a braking mechanism that terminates DAG-mediated signals. Two DGK isoforms, α and ζ, are expressed predominantly in T cells and synergistically regulate the development of both conventional αβ T cells and invariant natural killer T cells in the thymus. In mature T cells, the activity of these DGK isoforms aids in the maintenance of self-tolerance by preventing T-cell hyperactivation upon T cell receptor stimulation and by promoting T-cell anergy. In CD8 cells, reduced DGK activity is associated with enhanced primary responses against viruses and tumors. Recent work also has established an important role for DGK activity at the immune synapse and identified partners that modulate DGK function. In addition, emerging evidence points to previously unappreciated roles for DGK function in directional secretion and T-cell adhesion. This review describes the multitude of roles played by DGKs in T cell development and function and emphasizes recent advances in the field.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Wattenberg BW, Raben DM. Diacylglycerol kinases put the brakes on immune function. Science’s STKE: signal transduction knowledge environment. 2007 Aug 25;2007(398):pe43. - PubMed
-
- Rincon E, Gharbi SI, Santos-Mendoza T, Merida I. Diacylglycerol kinase zeta: at the crossroads of lipid signaling and protein complex organization. Prog Lipid Res. 2012 Jan;51(1):1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

