Manipulating the PD-1 pathway to improve immunity
- PMID: 23582509
- PMCID: PMC5946314
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2013.03.003
Manipulating the PD-1 pathway to improve immunity
Abstract
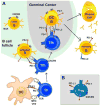
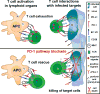
PD-1 is an inhibitory receptor induced in T cells by antigen stimulation and sustained PD-1 expression plays a key role in T cell dysfunction. Blocking PD-1 signaling rescues exhausted T cells and is an effective treatment for chronic infections and cancer. Nonetheless, combining PD-1 pathway blockade to therapeutic vaccination should further improve T cell rescue. PD-1 is induced shortly after T cell priming, but little is known about the role of PD-1 in the initiation of immune responses. In addition, the PD-1 pathway may also modulate humoral responses, since both B cells and Tfh cells express PD-1. Therefore, even though much progress has been achieved by manipulation of the PD-1 pathway to rescue exhausted T cells, this powerful immunotherapy could still be further exploited.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Jin HT, Ahmed R, Okazaki T. Role of PD-1 in regulating T-cell immunity. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2011;350:17–37. - PubMed
-
- Barber DL, Wherry EJ, Masopust D, Zhu B, Allison JP, Sharpe AH, Freeman GJ, Ahmed R. Restoring function in exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection. Nature. 2006;439:682–687. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

