Vinpocetine attenuates lipid accumulation and atherosclerosis formation
- PMID: 23583194
- PMCID: PMC3682500
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.03.092
Vinpocetine attenuates lipid accumulation and atherosclerosis formation
Abstract
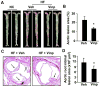
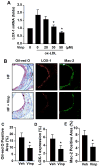
Atherosclerosis, the major cause of myocardial infarction and stroke, is a chronic arterial disease characterized by lipid deposition and inflammation in the vessel wall. Cholesterol, in low-density lipoprotein (LDL), plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Vinpocetine, a derivative of the alkaloid vincamine, has long been used as a cerebral blood flow enhancer for treating cognitive impairment. Recent study indicated that vinpocetine is a potent anti-inflammatory agent. However, its role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis remains unexplored. In the present study, we show that vinpocetine significantly reduced atherosclerotic lesion formation in ApoE knockout mice fed with a high-fat diet. In cultured murine macrophage RAW264.7 cells, vinpocetine markedly attenuated oxidized LDL (ox-LDL) uptake and foam cell formation. Moreover, vinpocetine greatly blocked the induction of ox-LDL receptor 1 (LOX-1) in cultured macrophages as well as in the LOX-1 level in atherosclerotic lesions. Taken together, our data reveal a novel role of vinpocetine in reduction of pathogenesis of atherosclerosis, at least partially through suppressing LOX-1 signaling pathway. Given the excellent safety profile of vinpocetine, this study suggests vinpocetine may be a therapeutic candidate for treating atherosclerosis.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibitory effects of vinpocetine on the progression of atherosclerosis are mediated by Akt/NF-κB dependent mechanisms in apoE-/- mice.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 9;8(12):e82509. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082509. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24349299 Free PMC article.
-
Statins Combined with AAV8-TBG-LOX-1 Reduce the Vascular Lipid-driven Inflammatory Response and Inhibit Atherosclerosis.Curr Med Sci. 2024 Dec;44(6):1097-1102. doi: 10.1007/s11596-024-2954-3. Epub 2024 Dec 4. Curr Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39627476
-
Hexarelin attenuates atherosclerosis via inhibiting LOX-1-NF-κB signaling pathway-mediated macrophage ox-LDL uptake in ApoE-/- mice.Peptides. 2019 Nov;121:170122. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2019.170122. Epub 2019 Aug 3. Peptides. 2019. PMID: 31386895
-
LOX-1, OxLDL, and atherosclerosis.Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:152786. doi: 10.1155/2013/152786. Epub 2013 Jul 10. Mediators Inflamm. 2013. PMID: 23935243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidized LDL, LOX-1 and atherosclerosis.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2011 Oct;25(5):419-29. doi: 10.1007/s10557-011-6341-5. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2011. PMID: 21947818 Review.
Cited by
-
Demonstration of the Protective Effect of Vinpocetine in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy.J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 8;13(16):4637. doi: 10.3390/jcm13164637. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39200779 Free PMC article.
-
Vinpocetine inhibits Streptococcus pneumoniae-induced upregulation of mucin MUC5AC expression via induction of MKP-1 phosphatase in the pathogenesis of otitis media.J Immunol. 2015 Jun 15;194(12):5990-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401489. Epub 2015 May 13. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25972475 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuated effects of topical vinpocetine in an imiquimod-induced mouse model of psoriasis.J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2023 Sep 20;19(1):35-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jtumed.2023.09.002. eCollection 2024 Feb. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37868105 Free PMC article.
-
Vinpocetine protects against the development of experimental abdominal aortic aneurysms.Clin Sci (Lond). 2020 Nov 27;134(22):2959-2976. doi: 10.1042/CS20201057. Clin Sci (Lond). 2020. PMID: 33111936 Free PMC article.
-
The anti-inflammatory properties of vinpocetine mediates its therapeutic potential in management of atherosclerosis.J Inflamm (Lond). 2024 Jun 10;21(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s12950-024-00394-x. J Inflamm (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38858751 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: A perspective for the 1990s. Nature. 1993;362:801–809. - PubMed
-
- Ross R. INFLAMMATION OR ATHEROGENESIS. New England Journal of Medicine. 1999;340:115–126. - PubMed
-
- Libby P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature. 2002;420:868–74. - PubMed
-
- Ballantyne CM. Low-density lipoproteins and risk for coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. 1998;82:3Q–12Q. - PubMed
-
- Halcox JP, Deanfield JE. Beyond the laboratory: clinical implications for statin pleiotropy. Circulation. 2004;109:II42–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

