Acute kidney injury in patients with cirrhosis: perils and promise
- PMID: 23583467
- PMCID: PMC3840046
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.03.018
Acute kidney injury in patients with cirrhosis: perils and promise
Abstract
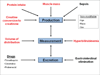
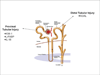
A 62-year-old man with cirrhosis secondary to hepatitis C and chronic alcohol abuse was admitted to the intensive care unit with hematemesis and mental status changes. Physical examination showed ascites and stigmata of chronic liver disease. Blood pressure was noted as 87/42 mm Hg and laboratory studies showed a serum creatinine level of 0.8 mg/dL, an estimated glomerular filtration rate of 84 mL/min/1.73 m(2) calculated using the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study equation, a serum sodium level of 123 mEq/L, a total serum bilirubin level of 4.3 mg/dL, and an international normalization ratio of 1.6. The patient was resuscitated with packed red blood cells and fresh-frozen plasma and bleeding was controlled. However, on the third day of admission, creatinine level increased to 1.5 mg/dL. Examination of urine sediment showed 1 to 5 bilirubin-stained granular casts per high-powered field and a few renal tubular epithelial cells. The urine sodium level was 21 mEq/L and the fractional excretion of sodium was 0.43%.
Keywords: AKI; AKIN; ATN; Acute Kidney Injury Network; Acute Tubular Necrosis; Ascites; CKD; Cirrhosis; FENa; GFR; HRS; Hepatorenal; IAC; ICU; International Ascites Club; KIM-1; Kidney Injury; MDRD; Modification of Diet in Renal Disease; NGAL; OR; PRA; RAAS; Urinary Biomarkers; acute kidney injury; acute tubular necrosis; chronic kidney disease; fractional excretion of sodium; glomerular filtration rate; hepatorenal syndrome; intensive care unit; kidney injury molecule-1; neutrophil gelatinase–associated lipocalin; odds ratio; prerenal azotemia; renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
Copyright © 2013 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Garcia-Tsao G, Parikh CR, Viola A. Acute kidney injury in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2008;48:2064–2077. - PubMed
-
- Schrier RW, Arroyo V, Bernardi M, et al. Peripheral arterial vasodilation hypothesis: a proposal for the initiation of renal sodium and water retention in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1988;8:1151–1157. - PubMed
-
- Lee FY, Colombato LA, Albillos A, et al. Nw-nitro-L-arginine administration corrects peripheral vasodilation and systemic capillary hypotension, and ameliorates plasma volume expansion and sodium retention in portal hypertensive rats. Hepatology. 1993;17:84–90. - PubMed
-
- Mejias M, Garcia-Pras E, Tiani C, et al. Beneficial effects of sorafenib on splanchnic, intrahepatic, and portocollateral circulations in portal hypertensive and cirrhotic rats. Hepatology. 2009;49(4):1245–1256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

