Identification of heart rate-associated loci and their effects on cardiac conduction and rhythm disorders
- PMID: 23583979
- PMCID: PMC3696959
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.2610
Identification of heart rate-associated loci and their effects on cardiac conduction and rhythm disorders
Abstract
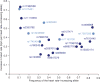
Elevated resting heart rate is associated with greater risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality. In a 2-stage meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies in up to 181,171 individuals, we identified 14 new loci associated with heart rate and confirmed associations with all 7 previously established loci. Experimental downregulation of gene expression in Drosophila melanogaster and Danio rerio identified 20 genes at 11 loci that are relevant for heart rate regulation and highlight a role for genes involved in signal transmission, embryonic cardiac development and the pathophysiology of dilated cardiomyopathy, congenital heart failure and/or sudden cardiac death. In addition, genetic susceptibility to increased heart rate is associated with altered cardiac conduction and reduced risk of sick sinus syndrome, and both heart rate-increasing and heart rate-decreasing variants associate with risk of atrial fibrillation. Our findings provide fresh insights into the mechanisms regulating heart rate and identify new therapeutic targets.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING FINANCIAL INTERESTS
The authors declare competing financial interests: details are available in the online version of the paper.
Figures
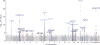
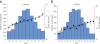

References
-
- Dyer AR, et al. Heart rate as a prognostic factor for coronary heart disease and mortality: findings in three Chicago epidemiologic studies. Am J Epidemiol. 1980;112:736–749. - PubMed
-
- Gillum RF, Makuc DM, Feldman JJ. Pulse rate, coronary heart disease, and death: the NHANES I Epidemiologic Follow-up Study. Am Heart J. 1991;121:172–177. - PubMed
-
- Nauman J, Janszky I, Vatten LJ, Wisloff U. Temporal changes in resting heart rate and deaths from ischemic heart disease. J Am Med Assoc. 2011;306:2579–2587. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz PJ, Billman GE, Stone HL. Autonomic mechanisms in ventricular fibrillation induced by myocardial ischemia during exercise in dogs with healed myocardial infarction. An experimental preparation for sudden cardiac death. Circulation. 1984;69:790–800. - PubMed
-
- Beere PA, Glagov S, Zarins CK. Retarding effect of lowered heart rate on coronary atherosclerosis. Science. 1984;226:180–182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- CZB/4/710/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- G0801056/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12013/3/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G1000143/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U106179471/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0401527/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U127592696/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U106188470/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- PG/12/38/29615/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- G9815508/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K24 HL105780/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092217/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0600705/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UP_A100_1003/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U19 HL065962/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 092731/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- T32 GM007753/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U106179473/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- UL1 TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL090620/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12015/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R21 DA026982/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_15018/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U123092720/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U106179472/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G1002084/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_U127592696/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12013/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL111314/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HL094535/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12013/4/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_U127561128/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

