Illuminating cancer systems with genetically engineered mouse models and coupled luciferase reporters in vivo
- PMID: 23585416
- PMCID: PMC3679270
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0503
Illuminating cancer systems with genetically engineered mouse models and coupled luciferase reporters in vivo
Abstract
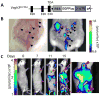
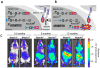
Bioluminescent imaging (BLI) is a powerful noninvasive tool that has dramatically accelerated the in vivo interrogation of cancer systems and longitudinal analysis of mouse models of cancer over the past decade. Various luciferase enzymes have been genetically engineered into mouse models (GEMM) of cancer, which permit investigation of cellular and molecular events associated with oncogenic transcription, posttranslational processing, protein-protein interactions, transformation, and oncogene addiction in live cells and animals. Luciferase-coupled GEMMs ultimately serve as a noninvasive, repetitive, longitudinal, and physiologic means by which cancer systems and therapeutic responses can be investigated accurately within the autochthonous context of a living animal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In vivo bioluminescent imaging (BLI): noninvasive visualization and interrogation of biological processes in living animals.Sensors (Basel). 2011;11(1):180-206. doi: 10.3390/s110100180. Epub 2010 Dec 28. Sensors (Basel). 2011. PMID: 22346573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioluminescent imaging: a critical tool in pre-clinical oncology research.J Pathol. 2010 Feb;220(3):317-27. doi: 10.1002/path.2656. J Pathol. 2010. PMID: 19967724 Review.
-
Quantitative bioluminescence imaging of mouse tumor models.Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2015 Jan 5;2015(1):pdb.prot078261. doi: 10.1101/pdb.prot078261. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2015. PMID: 25561617
-
A Cre/LoxP conditional luciferase reporter transgenic mouse for bioluminescence monitoring of tumorigenesis.Genesis. 2009 Oct;47(10):659-66. doi: 10.1002/dvg.20545. Genesis. 2009. PMID: 19603508
-
Bioluminescent imaging: emerging technology for non-invasive imaging of bone tissue engineering.Biomaterials. 2006 Mar;27(9):1851-8. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.09.034. Epub 2005 Oct 20. Biomaterials. 2006. PMID: 16242768 Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-Modal Multi-Spectral Intravital Microscopic Imaging of Signaling Dynamics in Real-Time during Tumor-ImmuneInteractions.Cells. 2021 Feb 26;10(3):499. doi: 10.3390/cells10030499. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33652682 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical Models of Brain Metastases in Breast Cancer.Biomedicines. 2022 Mar 13;10(3):667. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10030667. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35327469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular neuroimaging: the basics.Semin Roentgenol. 2014 Apr;49(2):225-33. doi: 10.1053/j.ro.2013.12.001. Epub 2013 Dec 13. Semin Roentgenol. 2014. PMID: 24836496 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Fluorophore-NanoLuc BRET Reporters Enable Sensitive In Vivo Optical Imaging and Flow Cytometry for Monitoring Tumorigenesis.Cancer Res. 2015 Dec 1;75(23):5023-33. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-3538. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26424696 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging of Preclinical Endometrial Cancer Models for Monitoring Tumor Progression and Response to Targeted Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Nov 27;11(12):1885. doi: 10.3390/cancers11121885. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31783595 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hanahan D, Coussens LM. Accessories to the crime: functions of cells recruited to the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell. 2012;21:309–22. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–74. - PubMed
-
- Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 2008;454:436–44. - PubMed
-
- Friedl P, Alexander S. Cancer invasion and the microenvironment: plasticity and reciprocity. Cell. 2011;147:992–1009. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

