Defining the Escherichia coli SecA dimer interface residues through in vivo site-specific photo-cross-linking
- PMID: 23585536
- PMCID: PMC3697251
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.02269-12
Defining the Escherichia coli SecA dimer interface residues through in vivo site-specific photo-cross-linking
Abstract
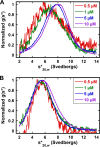
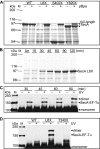
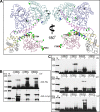
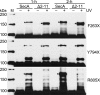
The motor protein SecA is a core component of the bacterial general secretory (Sec) pathway and is essential for cell viability. Despite evidence showing that SecA exists in a dynamic monomer-dimer equilibrium favoring the dimeric form in solution and in the cytoplasm, there is considerable debate as to the quaternary structural organization of the SecA dimer. Here, a site-directed photo-cross-linking technique was utilized to identify residues on the Escherichia coli SecA (ecSecA) dimer interface in the cytosol of intact cells. The feasibility of this method was demonstrated with residue Leu6, which is essential for ecSecA dimerization based on our analytical ultracentrifugation studies of SecA L6A and shown to form the cross-linked SecA dimer in vivo with p-benzoyl-phenylalanine (pBpa) substituted at position 6. Subsequently, the amino terminus (residues 2 to 11) in the nucleotide binding domain (NBD), Phe263 in the preprotein binding domain (PBD), and Tyr794 and Arg805 in the intramolecular regulator of the ATPase 1 domain (IRA1) were identified to be involved in ecSecA dimerization. Furthermore, the incorporation of pBpa at position 805 did not form a cross-linked dimer in the SecA Δ2-11 context, indicating the possibility that the amino terminus may directly contact Arg805 or that the deletion of residues 2 to 11 alters the topology of the naturally occurring ecSecA dimer.
Figures

References
-
- Papanikou E, Karamanou S, Economou A. 2007. Bacterial protein secretion through the translocase nanomachine. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 5:839–851 - PubMed
-
- Fekkes P, de Wit JG, van der Wolk JP, Kimsey HH, Kumamoto CA, Driessen AJ. 1998. Preprotein transfer to the Escherichia coli translocase requires the co-operative binding of SecB and the signal sequence to SecA. Mol. Microbiol. 29:1179–1190 - PubMed
-
- Economou A, Wickner W. 1994. SecA promotes preprotein translocation by undergoing ATP-driven cycles of membrane insertion and deinsertion. Cell 78:835–843 - PubMed
-
- Papanikolau Y, Papadovasilaki M, Ravelli RBG, McCarthy AA, Cusack S, Economou A, Petratos K. 2007. Structure of dimeric SecA, the Escherichia coli preprotein translocase motor. J. Mol. Biol. 366:1545–1557 - PubMed
-
- Cabelli RJ, Dolan KM, Qian LP, Oliver DB. 1991. Characterization of membrane-associated and soluble states of SecA protein from wild-type and SecA51(TS) mutant strains of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 266:24420–24427 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

