Non ionising radiation as a non chemical strategy in regenerative medicine: Ca(2+)-ICR "In Vitro" effect on neuronal differentiation and tumorigenicity modulation in NT2 cells
- PMID: 23585910
- PMCID: PMC3621667
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061535
Non ionising radiation as a non chemical strategy in regenerative medicine: Ca(2+)-ICR "In Vitro" effect on neuronal differentiation and tumorigenicity modulation in NT2 cells
Abstract
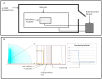
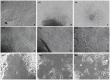
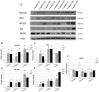
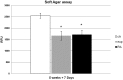
In regenerative medicine finding a new method for cell differentiation without pharmacological treatment or gene modification and minimal cell manipulation is a challenging goal. In this work we reported a neuronal induced differentiation and consequent reduction of tumorigenicity in NT2 human pluripotent embryonal carcinoma cells exposed to an extremely low frequency electromagnetic field (ELF-EMF), matching the cyclotron frequency corresponding to the charge/mass ratio of calcium ion (Ca(2+)-ICR). These cells, capable of differentiating into post-mitotic neurons following treatment with Retinoic Acid (RA), were placed in a solenoid and exposed for 5 weeks to Ca(2+)-ICR. The solenoid was installed in a μ-metal shielded room to avoid the effect of the geomagnetic field and obtained totally controlled and reproducible conditions. Contrast microscopy analysis reveled, in the NT2 exposed cells, an important change in shape and morphology with the outgrowth of neuritic-like structures together with a lower proliferation rate and metabolic activity alike those found in the RA treated cells. A significant up-regulation of early and late neuronal differentiation markers and a significant down-regulation of the transforming growth factor-α (TGF-α) and the fibroblast growth factor-4 (FGF-4) were also observed in the exposed cells. The decreased protein expression of the transforming gene Cripto-1 and the reduced capability of the exposed NT2 cells to form colonies in soft agar supported these last results. In conclusion, our findings demonstrate that the Ca(2+)-ICR frequency is able to induce differentiation and reduction of tumorigenicity in NT2 exposed cells suggesting a new potential therapeutic use in regenerative medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Megiorni F, Mora B, Indovina P, Mazzilli MC (2005) Expression of neuronal markers during NTera2/cloneD1 differentiation by cell aggregation method. Neurosci Lett 373: 105–109. - PubMed
-
- Stanke M, Stubbusch J, Rohrer H (2004) Interaction of Mash1 and Phox2b in sympathetic neuron development. Mol Cell Neurosci 25: 374–382. - PubMed
-
- Podrygajlo G, Tegenge MA, Gierse A, Paquet-Durand F, Tan S, et al. (2009) Cellular phenotypes of human model neurons (NT2) after differentiation in aggregate culture. Cell Tissue Res 336: 439–452. - PubMed
-
- Gao ZY, Xu G, Stwora-Wojczyk MM, Matschinsky FM, Lee VM, et al. (1998) Retinoic acid induction of calcium channel expression in human NT2N neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 247: 407–413. - PubMed
-
- Neelands TR, King AP, Macdonald RL (2000) Functional expression of L-, N-, P/Q-, and R-type calcium channels in the human NT2-N cell line. J Neurophysiol 84: 2933–2944. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

