Early diagnosis of lung cancer
- PMID: 23585930
- PMCID: PMC3616602
- DOI: 10.12703/P5-12
Early diagnosis of lung cancer
Abstract
A large randomized controlled trial, The National Lung Screening Study (NLST), has demonstrated that screening with low-dose spiral computed tomography saved lives from lung cancer when compared with screening with chest radiographs. This is the first test showing efficacy in screening for lung cancer as previous trials of chest radiographs and sputum cytology failed to result in fewer deaths with screening. This review will examine the problem of lung cancer, the issues presented by screening, and the results of computed tomography (CT) studies for lung cancer screening. Now that CT screening has been shown to be effective, implementation of screening becomes the next step.
Figures
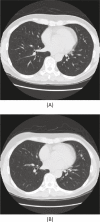
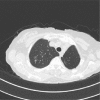
References
-
- Goldstraw P, Crowley J, Chansky K, Giroux DJ, Groome PA, Rami-Porta R, Postmus PE, Rusch V, Sobin L. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: proposals for the revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the TNM Classification of malignant tumours. J Thorac Oncol. 2007;2:706–14. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31812f3c1a. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Frost JK, Ball WC, Levin ML, Tockman MS, Baker RR, Carter D, Eggleston JC, Erozan YS, Gupta PK, Khouri NF. Early lung cancer detection: results of the initial (prevalence) radiologic and cytologic screening in the Johns Hopkins study. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984;130:549–54. - PubMed
-
- Flehinger BJ, Melamed MR, Zaman MB, Heelan RT, Perchick WB, Martini N. Early lung cancer detection: results of the initial (prevalence) radiologic and cytologic screening in the Memorial Sloan-Kettering study. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984;130:555–60. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

