Skin basement membrane: the foundation of epidermal integrity--BM functions and diverse roles of bridging molecules nidogen and perlecan
- PMID: 23586018
- PMCID: PMC3618921
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/179784
Skin basement membrane: the foundation of epidermal integrity--BM functions and diverse roles of bridging molecules nidogen and perlecan
Abstract
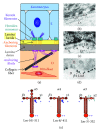
The epidermis functions in skin as first defense line or barrier against environmental impacts, resting on extracellular matrix (ECM) of the dermis underneath. Both compartments are connected by the basement membrane (BM), composed of a set of distinct glycoproteins and proteoglycans. Herein we are reviewing molecular aspects of BM structure, composition, and function regarding not only (i) the dermoepidermal interface but also (ii) the resident microvasculature, primarily focusing on the per se nonscaffold forming components perlecan and nidogen-1 and nidogen-2. Depletion or functional deficiencies of any BM component are lethal at some stage of development or around birth, though BM defects vary between organs and tissues. Lethality problems were overcome by developmental stage- and skin-specific gene targeting or by cell grafting and organotypic (3D) cocultures of normal or defective cells, which allows recapitulating BM formation de novo. Thus, evidence is accumulating that BM assembly and turnover rely on mechanical properties and composition of the adjacent ECM and the dynamics of molecular assembly, including further "minor" local components, nidogens largely functioning as catalysts or molecular adaptors and perlecan as bridging stabilizer. Collectively, orchestration of BM assembly, remodeling, and the role of individual players herein are determined by the developmental, tissue-specific, or functional context.
Figures

References
-
- Fuchs E, Raghavan S. Getting under the skin of epidermal morphogenesis. Nature Reviews Genetics. 2002;3(3):199–209. - PubMed
-
- Niessen CM. Tight junctions/adherens junctions: basic structure and function. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 2007;127(11):2525–2532. - PubMed
-
- Hohl D, Lichti U, Breitkreutz D, Steinert PM, Roop DR. Transcription of the human loricrin gene in vitro is induced by calcium and cell density and suppressed by retinoic acid. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 1991;96(4):414–418. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

