Structure-activity relationships of pentamidine-affected ion channel trafficking and dofetilide mediated rescue
- PMID: 23586323
- PMCID: PMC3831711
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.12208
Structure-activity relationships of pentamidine-affected ion channel trafficking and dofetilide mediated rescue
Abstract
Background and purpose: Drug interference with normal hERG protein trafficking substantially reduces the channel density in the plasma membrane and thereby poses an arrhythmic threat. The chemical substructures important for hERG trafficking inhibition were investigated using pentamidine as a model drug. Furthermore, the relationship between acute ion channel block and correction of trafficking by dofetilide was studied.
Experimental approach: hERG and K(IR)2.1 trafficking in HEK293 cells was evaluated by Western blot and immunofluorescence microscopy after treatment with pentamidine and six pentamidine analogues, and correction with dofetilide and four dofetilide analogues that displayed different abilities to inhibit IKr . Molecular dynamics simulations were used to address mode, number and type of interactions between hERG and dofetilide analogues.
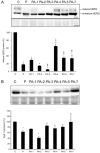
Key results: Structural modifications of pentamidine differentially affected plasma membrane levels of hERG and K(IR)2.1. Modification of the phenyl ring or substituents directly attached to it had the largest effect, affirming the importance of these chemical residues in ion channel binding. PA-4 had the mildest effects on both ion channels. Dofetilide corrected pentamidine-induced hERG, but not K(IR)2.1 trafficking defects. Dofetilide analogues that displayed high channel affinity, mediated by pi-pi stacks and hydrophobic interactions, also restored hERG protein levels, whereas analogues with low affinity were ineffective.
Conclusions and implications: Drug-induced trafficking defects can be minimized if certain chemical features are avoided or 'synthesized out'; this could influence the design and development of future drugs. Further analysis of such features in hERG trafficking correctors may facilitate the design of a non-blocking corrector for trafficking defective hERG proteins in both congenital and acquired LQTS.
© 2013 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures



Similar articles
-
LUF7244 plus Dofetilide Rescues Aberrant Kv11.1 Trafficking and Produces Functional IKv11.1.Mol Pharmacol. 2020 Jun;97(6):355-364. doi: 10.1124/mol.119.118190. Epub 2020 Apr 2. Mol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32241959
-
Exploring chemical substructures essential for HERG k(+) channel blockade by synthesis and biological evaluation of dofetilide analogues.ChemMedChem. 2009 Oct;4(10):1722-32. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.200900203. ChemMedChem. 2009. PMID: 19725081
-
Molecular determinants of dofetilide block of HERG K+ channels.Circ Res. 1998 Feb 23;82(3):386-95. doi: 10.1161/01.res.82.3.386. Circ Res. 1998. PMID: 9486667
-
The cardiac hERG/IKr potassium channel as pharmacological target: structure, function, regulation, and clinical applications.Curr Pharm Des. 2006;12(18):2271-83. doi: 10.2174/138161206777585102. Curr Pharm Des. 2006. PMID: 16787254 Review.
-
[HERG K+ channel, the target of anti-arrhythmias drugs].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2007 Jul;42(7):687-91. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2007. PMID: 17882949 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Quantitative Profiling of the Effects of Vanoxerine on Human Cardiac Ion Channels and its Application to Cardiac Risk.Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 30;5:17623. doi: 10.1038/srep17623. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26616666 Free PMC article.
-
Pentamidine Inhibits Ovarian Cancer Cell Proliferation and Migration by Maintaining Stability of PTEN in vitro.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 Jul 1;15:2857-2868. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S311187. eCollection 2021. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021. PMID: 34234416 Free PMC article.
-
Translational toxicology and rescue strategies of the hERG channel dysfunction: biochemical and molecular mechanistic aspects.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014 Dec;35(12):1473-84. doi: 10.1038/aps.2014.101. Epub 2014 Nov 24. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014. PMID: 25418379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug-likeness of linear pentamidine analogues and their impact on the hERG K+ channel - correlation with structural features.RSC Adv. 2019 Dec 2;9(66):38355-38371. doi: 10.1039/c9ra08404e. eCollection 2019 Nov 25. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35540224 Free PMC article.
-
Ion channel traffic jams: the significance of trafficking deficiency in long QT syndrome.Cell Discov. 2025 Jan 10;11(1):3. doi: 10.1038/s41421-024-00738-0. Cell Discov. 2025. PMID: 39788950 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson CL, Delisle BP, Anson BD, Kilby JA, Will ML, Tester DJ, et al. Most LQT2 mutations reduce Kv11.1 (hERG) current by a class 2 (trafficking-deficient) mechanism. Circulation. 2006;113:365–373. - PubMed
-
- Bakunova SM, Bakunov SA, Patrick DA, Kumar EV, Ohemeng KA, Bridges AS, et al. Structure-activity study of pentamidine analogues as antiprotozoal agents. J Med Chem. 2009a;52:2016–2035. - PubMed
-
- Bakunova SM, Bakunov SA, Wenzler T, Barszcz T, Werbovetz KA, Brun R, et al. Synthesis and antiprotozoal activity of pyridyl analogues of pentamidine. J Med Chem. 2009b;52:4657–4667. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

