Rapid plasmid replicon typing by real time PCR melting curve analysis
- PMID: 23586392
- PMCID: PMC3639092
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-13-83
Rapid plasmid replicon typing by real time PCR melting curve analysis
Abstract
Background: Genes encoding Extended Spectrum Beta Lactamases are usually located on transferable plasmids. Each plasmid contains its own replication mechanism. Carattoli et al. developed an extended PCR-based replicon typing method to characterize and identify the replicons of the major plasmid incompatibility groups in Enterobacteriaceae. Based on this method, we designed a rapid approach with amplicon detection by real-time melting curve analysis. This method appeared to be fast, sensitive, less laborious, less prone to contamination and applicable in a routine laboratory environment.
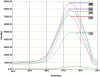
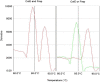
Results: We successfully integrated the post-PCR analysis of the replicon typing into a closed system, which leads to a 10-fold increase in sensitivity compared to agarose gel visualization. Moreover, the use of crude lysates and SYBR-green saves a considerable amount of hands-on time without decreasing the sensitivity or specificity.
Conclusions: This real-time melting curve replicon typing method appears to be fast, sensitive, less laborious, less prone to contamination and applicable in a routine laboratory environment.
Figures
References
-
- Coque TM, Baquero F, Canton R. Increasing prevalence of ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae in Europe. Euro Surveill. 2008;13:19044. - PubMed
-
- Boyd DA, Tyler S, Christianson S, McGeer A, Muller MP, Willey BM, Bryce E, Gardam M, Nordmann P, Mulvey MR. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 92-kilobase plasmid harboring the CTX-M-15 extended-spectrum beta-lactamase involved in an outbreak in long-term-care facilities in Toronto, Canada. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48:3758–3764. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.10.3758-3764.2004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

