Titanium dioxide nanoparticles: a review of current toxicological data
- PMID: 23587290
- PMCID: PMC3637140
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-8977-10-15
Titanium dioxide nanoparticles: a review of current toxicological data
Abstract
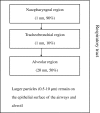
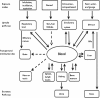
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles (NPs) are manufactured worldwide in large quantities for use in a wide range of applications. TiO2 NPs possess different physicochemical properties compared to their fine particle (FP) analogs, which might alter their bioactivity. Most of the literature cited here has focused on the respiratory system, showing the importance of inhalation as the primary route for TiO2 NP exposure in the workplace. TiO2 NPs may translocate to systemic organs from the lung and gastrointestinal tract (GIT) although the rate of translocation appears low. There have also been studies focusing on other potential routes of human exposure. Oral exposure mainly occurs through food products containing TiO2 NP-additives. Most dermal exposure studies, whether in vivo or in vitro, report that TiO2 NPs do not penetrate the stratum corneum (SC). In the field of nanomedicine, intravenous injection can deliver TiO2 nanoparticulate carriers directly into the human body. Upon intravenous exposure, TiO2 NPs can induce pathological lesions of the liver, spleen, kidneys, and brain. We have also shown here that most of these effects may be due to the use of very high doses of TiO2 NPs. There is also an enormous lack of epidemiological data regarding TiO2 NPs in spite of its increased production and use. However, long-term inhalation studies in rats have reported lung tumors. This review summarizes the current knowledge on the toxicology of TiO2 NPs and points out areas where further information is needed.
Figures
References
-
- Kisin ER, Murray AR, Keane MJ, Shi XC, Schwegler-Berry D, Gorelik O, Arepalli S, Castranova V, Wallace WE, Kagan VE, Shvedova AA. Single-walled carbon nanotubes: geno- and cytotoxic effects in lung fibroblast V79 cells. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2007;70:2071–2079. doi: 10.1080/15287390701601251. - DOI - PubMed
-
- EU - European Commission Recommendation on the definition of nanomaterial. http://osha.europa.eu/en/news/eu-european-commission-recommendation-on-t....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

