CD40 immunotherapy for pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 23589109
- PMCID: PMC3731141
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-013-1427-5
CD40 immunotherapy for pancreatic cancer
Abstract
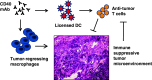
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA) is a highly aggressive and lethal cancer which is poorly responsive to standard therapies. Although the PDA tumor microenvironment is considered especially immunosuppressive, recent data mostly from genetically engineered and other mouse models of the disease suggest that novel immunotherapeutic approaches hold promise. Here, we describe both laboratory and clinical efforts to target the CD40 pathway for immunotherapy in PDA. Findings suggest that CD40 agonists can mediate both T-cell-dependent and T-cell-independent immune mechanisms of tumor regression in mice and patients. T-cell-independent mechanisms are associated with macrophage activation and the destruction of PDA tumor stroma, supporting the concept that immune modulation of the tumor microenvironment represents a useful approach in cancer immunotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- van Kooten C, Banchereau J. CD40–CD40 ligand. J Leukoc Biol. 2000;67(1):2–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

