Tsutsugamushi disease caused by Shimokoshi-type Orientia tsutsugamushi: the first report in Western Japan
- PMID: 23589529
- PMCID: PMC3752827
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.12-0740
Tsutsugamushi disease caused by Shimokoshi-type Orientia tsutsugamushi: the first report in Western Japan
Abstract
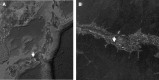
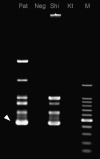
An 85-year-old female farmer was admitted to our hospital for fever, general fatigue, and skin rash. Cephalosporin was not effective and minocycline was dramatically effective. An eschar was discovered on her inguinal region after the defervescence. Laboratory examination of serum taken 12 days after onset of the illness showed elevated titers of antibodies against the Shimokoshi strain of Orientia tsutsugamushi. The gene sequence analysis of specimen from the patient's eschar revealed high similarity to the Shimokoshi strain by nested polymerase chain reaction. Therefore, this patient was diagnosed as a case of Shimokoshi-type tsutsugamushi disease, which has not previously been reported in Western Japan. Recently, cases of this type have also been confirmed in northeastern Japan, suggesting the need for further epidemiological studies.
Figures

References
-
- Rajapakse S, Rodrigo C, Fernando D. Scrub typhus: pathophysiology, clinical manifestations and prognosis. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2012;5:261–264. - PubMed
-
- Botelho-Nevers E, Raoult D. Fever of unknown origin due to rickettsioses. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2007;21:997–1011. - PubMed
-
- Blacksell SD, Bryant NJ, Paris DH, Doust JA, Sakoda Y, Day NP. Scrub typhus serologic testing with the indirect immunofluorescence method as a diagnostic gold standard: a lack of consensus leads to a lot of confusion. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44:391–401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

