HP1 promotes tumor suppressor BRCA1 functions during the DNA damage response
- PMID: 23589625
- PMCID: PMC3675466
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt231
HP1 promotes tumor suppressor BRCA1 functions during the DNA damage response
Abstract
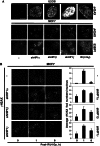
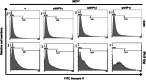
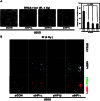
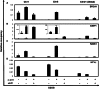
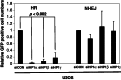
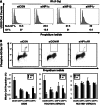
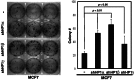
The DNA damage response (DDR) involves both the control of DNA damage repair and signaling to cell cycle checkpoints. Therefore, unraveling the underlying mechanisms of the DDR is important for understanding tumor suppression and cellular resistance to clastogenic cancer therapeutics. Because the DDR is likely to be influenced by chromatin regulation at the sites of DNA damage, we investigated the role of heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) during the DDR process. We monitored double-strand breaks (DSBs) using the γH2AX foci marker and found that depleting cells of HP1 caused genotoxic stress, a delay in the repair of DSBs and elevated levels of apoptosis after irradiation. Furthermore, we found that these defects in repair were associated with impaired BRCA1 function. Depleting HP1 reduced recruitment of BRCA1 to DSBs and caused defects in two BRCA1-mediated DDR events: (i) the homologous recombination repair pathway and (ii) the arrest of cell cycle at the G2/M checkpoint. In contrast, depleting HP1 from cells did not affect the non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) pathway: instead it elevated the recruitment of the 53BP1 NHEJ factor to DSBs. Notably, all three subtypes of HP1 seemed to be almost equally important for these DDR functions. We suggest that the dynamic interaction of HP1 with chromatin and other DDR factors could determine DNA repair choice and cell fate after DNA damage. We also suggest that compromising HP1 expression could promote tumorigenesis by impairing the function of the BRCA1 tumor suppressor.
Figures

References
-
- Goldberg AD, Allis CD, Bernstein E. Epigenetics: a landscape takes shape. Cell. 2007;128:635–638. - PubMed
-
- Cheung P, Allis CD, Sassone-Corsi P. Signaling to chromatin through histone modifications. Cell. 2000;103:263–271. - PubMed
-
- Bannister AJ, Zegerman P, Partridge JF, Miska EA, Thomas JO, Allshire RC, Kouzarides T. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature. 2001;410:120–124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

