Diurnal choroidal thickness changes in normal eyes of Turkish people measured by spectral domain optical coherence tomography
- PMID: 23589769
- PMCID: PMC3622386
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/687165
Diurnal choroidal thickness changes in normal eyes of Turkish people measured by spectral domain optical coherence tomography
Abstract
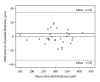
Purpose. To analyse the diurnal variation of central choroidal thickness (CCT) in healthy emetropic patients during working hours. Methods. Fifty healthy young emmetrpic volunteers were included in this study. CCT was measured at 9 AM and 4 PM with spectral domain optical coherence tomography (Spectralis, Heidelberg Engineering) with enhanced depth imaging. Diurnal variation of CCT, the correlation between rigth and left eyes and the demographic factors affecting this variation were assessed. Findings. The mean CCT at 9 AM and 4 PM was 308.7 ± 64.5 μ m and 308.7 ± 62 μ m, respectively, with a mean diurnal amplitude of -0.03 ± 14.7 μ m, ranging between -55 μ m and 47 μ m, the difference was statistically insignificant (P: 0.9). There were positive correlations between right and left eyes among CCT measurements at 9 AM, 4 PM and the mean amplitude of diurnal change (r: 0.65, P < 0.01; r: 0.60, P < 0.01; r: 0.45, P: 0.00, resp.). There was a statistically significant negative correlation between the magnitude of diurnal change and age (r: -0.27, P: 0.01). Conclusion. Although the mean CCT in the all group does not show significant variation during working hours, the pattern of diurnal variation may vary from person to person according to age, and there is a great harmony between the two eyes.
Figures
References
-
- Spaide RF, Koizumi H, Pozonni MC. Enhanced depth imaging spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. American Journal of Ophthalmology. 2008;146(4):496–500. - PubMed
-
- Imamura Y, Fujiwara T, Margolis R, Spaide RF. Enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography of the choroid in central serous chorioretinopathy. Retina. 2009;29(10):1469–1473. - PubMed
-
- Kim SW, Oh J, Kwon SS, Yoo J, Huh K. Comparison of choroidal thickness among patients with healthy eyes, early age-related maculopathy, neaovascular age-related macular degeneration, central serous chorioretinopathy and polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Retina. 2011;31:1904–1911. - PubMed
-
- Wood A, Binns A, Margrain T, et al. Retinal and choroidal thickness in early age-related macular degeneration. American Journal of Ophthalmology. 2011;152:1030–1038. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials