Crystal structure of a prokaryotic (6-4) photolyase with an Fe-S cluster and a 6,7-dimethyl-8-ribityllumazine antenna chromophore
- PMID: 23589886
- PMCID: PMC3645588
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1302377110
Crystal structure of a prokaryotic (6-4) photolyase with an Fe-S cluster and a 6,7-dimethyl-8-ribityllumazine antenna chromophore
Abstract
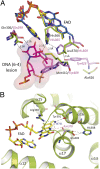
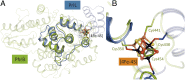
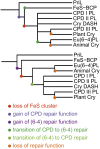
The (6-4) photolyases use blue light to reverse UV-induced (6-4) photoproducts in DNA. This (6-4) photorepair was thought to be restricted to eukaryotes. Here we report a prokaryotic (6-4) photolyase, PhrB from Agrobacterium tumefaciens, and propose that (6-4) photolyases are broadly distributed in prokaryotes. The crystal structure of photolyase related protein B (PhrB) at 1.45 Å resolution suggests a DNA binding mode different from that of the eukaryotic counterparts. A His-His-X-X-Arg motif is located within the proposed DNA lesion contact site of PhrB. This motif is structurally conserved in eukaryotic (6-4) photolyases for which the second His is essential for the (6-4) photolyase function. The PhrB structure contains 6,7-dimethyl-8-ribityllumazine as an antenna chromophore and a [4Fe-4S] cluster bound to the catalytic domain. A significant part of the Fe-S fold strikingly resembles that of the large subunit of eukaryotic and archaeal primases, suggesting that the PhrB-like photolyases branched at the base of the evolution of the cryptochrome/photolyase family. Our study presents a unique prokaryotic (6-4) photolyase and proposes that the prokaryotic (6-4) photolyases are the ancestors of the cryptochrome/photolyase family.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Sancar A. Structure and function of DNA photolyase and cryptochrome blue-light photoreceptors. Chem Rev. 2003;103(6):2203–2237. - PubMed
-
- Cashmore AR. Cryptochromes: Enabling plants and animals to determine circadian time. Cell. 2003;114(5):537–543. - PubMed
-
- Chaves I, et al. The cryptochromes: Blue light photoreceptors in plants and animals. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2011;62:335–364. - PubMed
-
- Essen LO. Photolyases and cryptochromes: Common mechanisms of DNA repair and light-driven signaling? Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2006;16(1):51–59. - PubMed
-
- Müller M, Carell T. Structural biology of DNA photolyases and cryptochromes. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2009;19(3):277–285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

