Preparation, purification and regioselective functionalization of protoescigenin--the main aglycone of escin complex
- PMID: 23591921
- PMCID: PMC6270381
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules18044389
Preparation, purification and regioselective functionalization of protoescigenin--the main aglycone of escin complex
Abstract
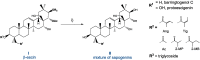
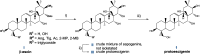
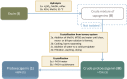
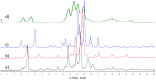
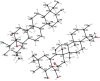
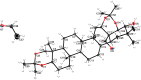
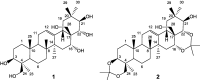
A two-step chemical process for controlled degradation of escin, affording a mixture of olean-12-ene sapogenins, was elaborated and scaled up. The main component of the mixture--protoescigenin--was isolated and purified, in the form of its corresponding monohydrate, without resource to chromatographic methods. This material was further converted into the high purity 3,24;16,22-di-O,O-isopropylidene derivative in a validated large scale laboratory process.
Figures
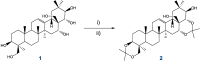
References
-
- Zhang Z., Li S., Lian X.-Y. An overview of genus Aesculus. L.: ethnobotany, phytochemistry, and pharmacological activities. Pharmac. Crops. 2010;1:24–51.
-
- Persson I.A.L., Persson K. Horse chesnut (Aesculus. hippocastanum L.) Recent Prog. Med. Plants. 2010;28:159–171.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

