Preventive pharmacologic treatments for episodic migraine in adults
- PMID: 23592242
- PMCID: PMC3744311
- DOI: 10.1007/s11606-013-2433-1
Preventive pharmacologic treatments for episodic migraine in adults
Abstract
Objectives: Systematic review of preventive pharmacologic treatments for community-dwelling adults with episodic migraine.
Data sources: Electronic databases through May 20, 2012.
Eligibility criteria: English-language randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of preventive drugs compared to placebo or active treatments examining rates of ≥50 % reduction in monthly migraine frequency or improvement in quality of life.
Study appraisal and synthesis methods: We assessed risk of bias and strength of evidence and conducted random effects meta-analyses of absolute risk differences and Bayesian network meta-analysis.
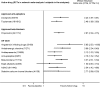
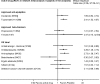
Results: Of 5,244 retrieved references, 215 publications of RCTs provided mostly low-strength evidence because of the risk of bias and imprecision. RCTs examined 59 drugs from 14 drug classes. All approved drugs, including topiramate (9 RCTs), divalproex (3 RCTs), timolol (3 RCTs), and propranolol (4 RCTs); off-label beta blockers metoprolol (4 RCTs), atenolol (1 RCT), nadolol (1 RCT), and acebutolol (1 RCT); angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors captopril (1 RCT) and lisinopril (1 RCT); and angiotensin II receptor blocker candesartan (1 RCT), outperformed placebo in reducing monthly migraine frequency by ≥50 % in 200-400 patients per 1,000 treated. Adverse effects leading to treatment discontinuation (68 RCTs) were greater with topiramate, off-label antiepileptics, and antidepressants than with placebo. Limited direct evidence as well as frequentist and exploratory network Bayesian meta-analysis showed no statistically significant differences in benefits between approved drugs. Off-label angiotensin-inhibiting drugs and beta-blockers were most effective and tolerable for episodic migraine prevention.
Limitations: We did not quantify reporting bias or contact principal investigators regarding unpublished trials.
Conclusions: Approved drugs prevented episodic migraine frequency by ≥50 % with no statistically significant difference between them. Exploratory network meta-analysis suggested that off-label angiotensin-inhibiting drugs and beta-blockers had favorable benefit-to-harm ratios. Evidence is lacking for long-term effects of drug treatments (i.e., trials of more than 3 months duration), especially for quality of life.
Figures
Comment in
-
Migraine prophylaxis: which drugs work and which ones don't.J Gen Intern Med. 2013 Sep;28(9):1125-6. doi: 10.1007/s11606-013-2469-2. J Gen Intern Med. 2013. PMID: 23636916 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
ACP Journal Club. Review: Approved and some off-label preventive drugs reduce migraine frequency in episodic migraine.Ann Intern Med. 2013 Oct 15;159(8):JC11. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-159-8-201310150-02011. Ann Intern Med. 2013. PMID: 24126660 No abstract available.
References
-
- Goadsby PJ, Raskin NH, et al. Chapter 15. Headache. In: Fauci AS, Braunwald E, Kasper DL, et al., editors. Harrison’s principles of internal medicine. 17. New York: The McGraw-Hill Companies; 2008.
-
- Diamond S, Bigal ME, Silberstein S, Loder E, Reed M, Lipton RB. Patterns of diagnosis and acute and preventive treatment for migraine in the United States: results from the American Migraine Prevalence and Prevention study. Headache. 2007;47:355–363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

