Doublecortin-like kinase 1 exhibits cancer stem cell-like characteristics in a human colon cancer cell line
- PMID: 23592893
- PMCID: PMC3626979
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.1000-9604.2013.03.02
Doublecortin-like kinase 1 exhibits cancer stem cell-like characteristics in a human colon cancer cell line
Abstract
Objective: Colon cancer stem cells (CSCs) are implicated in colorectal cancer carcinogenesis, metastasis, and therapeutic resistance. The identification of these cells could help to develop novel therapeutic strategies. Doublecortin-like kinase 1 (DCLK1) has been viewed as a marker for gastrointestinal stem cells that fuel the self-renewal process, however others view them as a marker of Tuft cells or as an enteroendocrine subtype. The purpose of this study was to use a colon cancer cell line to identify and characterize the stem-like characteristics of the DCLK1+ cell population.
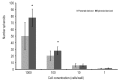
Methods: To enrich stem-like cells, HCT116 cells (derived from colon adenocarcinomas) were cultured using serum-free media to form spheres under both normal oxygen and hypoxia condition. DCLK1 transcript expression in the adherent parental cells and spheroids was quantified using quantitative real time reverse transcription- polymerase chain reaction [(q)RT-PCR]. DCLK1 protein expression was determined using flow cytometry. Self-renewal capability from adherent parental cells and spheroids was determined using extreme limiting dilution analysis (ELDA).
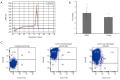
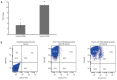
Results: Under both normal oxygen and hypoxia condition, the adherent parental cells were composed of cells that express low levels of DCLK1. However, spheroids exhibited an increased frequency of cells expressing DCLK1 on both mRNA and protein levels. Cells derived from spheroids also possess stronger self-renewal capability.
Conclusions: The higher fraction of DCLK1+ cells exhibited by spheroids and hypoxia reflects the stem-like characteristics of these cells. DCLK1 may represent an ideal marker to study and develop effective strategies to overcome chemo-resistance and relapse of colon cancer.
Keywords: Doublecortin-like kinase 1 (DCLK1); cancer stem cells; colorectal cancer; spheroids; stem cell marker.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tuft and Cancer Stem Cell Marker DCLK1: A New Target to Enhance Anti-Tumor Immunity in the Tumor Microenvironment.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Dec 17;12(12):3801. doi: 10.3390/cancers12123801. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33348546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting colon cancer stem cells using novel doublecortin like kinase 1 antibody functionalized folic acid conjugated hesperetin encapsulated chitosan nanoparticles.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022 Sep;217:112612. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2022.112612. Epub 2022 Jun 7. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022. PMID: 35738074
-
Sox9, Hopx, and survivin and tuft cell marker DCLK1 expression in normal canine intestine and in intestinal adenoma and adenocarcinoma.Vet Pathol. 2022 May;59(3):415-426. doi: 10.1177/03009858221079666. Epub 2022 Feb 26. Vet Pathol. 2022. PMID: 35220825
-
Alternative splice variants of DCLK1 mark cancer stem cells, promote self-renewal and drug-resistance, and can be targeted to inhibit tumorigenesis in kidney cancer.Int J Cancer. 2018 Sep 1;143(5):1162-1175. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31400. Epub 2018 Apr 16. Int J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29577277 Free PMC article.
-
DCLK1 and its interaction partners: An effective therapeutic target for colorectal cancer.Oncol Lett. 2021 Dec;22(6):850. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.13111. Epub 2021 Oct 26. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 34733368 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Doublecotin-Like Kinase 1 Increases Chemoresistance of Colorectal Cancer Cells through the Anti-Apoptosis Pathway.J Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;9(3):447. doi: 10.4172/2157-7633.1000447. Epub 2019 May 3. J Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31372308 Free PMC article.
-
Tuft and Cancer Stem Cell Marker DCLK1: A New Target to Enhance Anti-Tumor Immunity in the Tumor Microenvironment.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Dec 17;12(12):3801. doi: 10.3390/cancers12123801. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33348546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small molecule kinase inhibitor LRRK2-IN-1 demonstrates potent activity against colorectal and pancreatic cancer through inhibition of doublecortin-like kinase 1.Mol Cancer. 2014 May 6;13:103. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-103. Mol Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24885928 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of circulating cancer stem cell marker, DCLK1 but not Lgr5, in chemoradiotherapy-treated colorectal cancer patients.Tumour Biol. 2015 Jun;36(6):4801-10. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3132-9. Epub 2015 Jan 29. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 25631749
-
A new insight into cancer stem cell markers: Could local and circulating cancer stem cell markers correlate in colorectal cancer?Tumour Biol. 2016 Feb;37(2):2405-14. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3989-7. Epub 2015 Sep 17. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26383518
References
-
- Available online: http://www.cancer.org/acs/groups/cid/documents/webcontent/003096-pdf.pdf
-
- American Cancer Society. Colorectal Cancer Facts & Figures. Atlanta, Georgia: American Cancer Society, 2011-2013.
-
- De Dosso S, Sessa C, Saletti P.Adjuvant therapy for colon cancer: present and perspectives. Cancer Treat Rev 2009;35:160-6 - PubMed
-
- Kopetz S, Freitas D, Calabrich AF, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II colon cancer. Oncology (Williston Park) 2008;22:260-70; discussion 270, 273, 275. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
