IL-27 receptor signalling restricts the formation of pathogenic, terminally differentiated Th1 cells during malaria infection by repressing IL-12 dependent signals
- PMID: 23593003
- PMCID: PMC3623720
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003293
IL-27 receptor signalling restricts the formation of pathogenic, terminally differentiated Th1 cells during malaria infection by repressing IL-12 dependent signals
Abstract
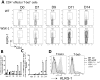
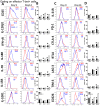
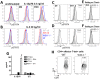
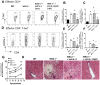
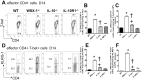
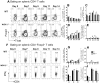
The IL-27R, WSX-1, is required to limit IFN-γ production by effector CD4⁺ T cells in a number of different inflammatory conditions but the molecular basis of WSX-1-mediated regulation of Th1 responses in vivo during infection has not been investigated in detail. In this study we demonstrate that WSX-1 signalling suppresses the development of pathogenic, terminally differentiated (KLRG-1⁺) Th1 cells during malaria infection and establishes a restrictive threshold to constrain the emergent Th1 response. Importantly, we show that WSX-1 regulates cell-intrinsic responsiveness to IL-12 and IL-2, but the fate of the effector CD4⁺ T cell pool during malaria infection is controlled primarily through IL-12 dependent signals. Finally, we show that WSX-1 regulates Th1 cell terminal differentiation during malaria infection through IL-10 and Foxp3 independent mechanisms; the kinetics and magnitude of the Th1 response, and the degree of Th1 cell terminal differentiation, were comparable in WT, IL-10R1⁻/⁻ and IL-10⁻/⁻ mice and the numbers and phenotype of Foxp3⁺ cells were largely unaltered in WSX-1⁻/⁻ mice during infection. As expected, depletion of Foxp3⁺ cells did not enhance Th1 cell polarisation or terminal differentiation during malaria infection. Our results significantly expand our understanding of how IL-27 regulates Th1 responses in vivo during inflammatory conditions and establishes WSX-1 as a critical and non-redundant regulator of the emergent Th1 effector response during malaria infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Christiaan J.M. Saris is a former employee of Amgen Inc. and owns stock and stock options in this company. Issued and pending Amgen patents on which he is a co-inventor are unrelated to the subject of this manuscript. This does not alter our adherence to all PLoS Pathogens policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures

References
-
- Hall AO, Silver JS, Hunter CA (2012) The immunobiology of IL-27. Adv Immunol 115: 1–44. - PubMed
-
- Yoshida H, Miyazaki Y (2008) Regulation of immune responses by interleukin-27. Immunol Rev 226: 234–247. - PubMed
-
- Villarino A, Hibbert L, Lieberman L, Wilson E, Mak T, et al. (2003) The IL-27R (WSX-1) is required to suppress T cell hyperactivity during infection. Immunity 19: 645–655. - PubMed
-
- Hamano S, Himeno K, Miyazaki Y, Ishii K, Yamanaka A, et al. (2003) WSX-1 is required for resistance to Trypanosoma cruzi infection by regulation of proinflammatory cytokine production. Immunity 19: 657–667. - PubMed
-
- Holscher C, Holscher A, Ruckerl D, Yoshimoto T, Yoshida H, et al. (2005) The IL-27 receptor chain WSX-1 differentially regulates antibacterial immunity and survival during experimental tuberculosis. J Immunol 174: 3534–3544. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- G0900487/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 004161/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/I020950/2/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- 020950/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/G004161/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

