Comparison of SIV and HIV-1 genomic RNA structures reveals impact of sequence evolution on conserved and non-conserved structural motifs
- PMID: 23593004
- PMCID: PMC3616985
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003294
Comparison of SIV and HIV-1 genomic RNA structures reveals impact of sequence evolution on conserved and non-conserved structural motifs
Abstract
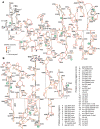
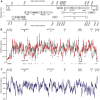
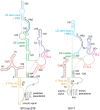
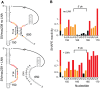
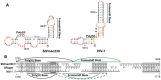
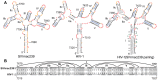
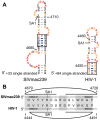
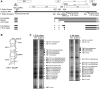
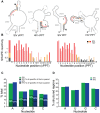
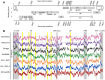
RNA secondary structure plays a central role in the replication and metabolism of all RNA viruses, including retroviruses like HIV-1. However, structures with known function represent only a fraction of the secondary structure reported for HIV-1(NL4-3). One tool to assess the importance of RNA structures is to examine their conservation over evolutionary time. To this end, we used SHAPE to model the secondary structure of a second primate lentiviral genome, SIVmac239, which shares only 50% sequence identity at the nucleotide level with HIV-1NL4-3. Only about half of the paired nucleotides are paired in both genomic RNAs and, across the genome, just 71 base pairs form with the same pairing partner in both genomes. On average the RNA secondary structure is thus evolving at a much faster rate than the sequence. Structure at the Gag-Pro-Pol frameshift site is maintained but in a significantly altered form, while the impact of selection for maintaining a protein binding interaction can be seen in the conservation of pairing partners in the small RRE stems where Rev binds. Structures that are conserved between SIVmac239 and HIV-1(NL4-3) also occur at the 5' polyadenylation sequence, in the plus strand primer sites, PPT and cPPT, and in the stem-loop structure that includes the first splice acceptor site. The two genomes are adenosine-rich and cytidine-poor. The structured regions are enriched in guanosines, while unpaired regions are enriched in adenosines, and functionaly important structures have stronger base pairing than nonconserved structures. We conclude that much of the secondary structure is the result of fortuitous pairing in a metastable state that reforms during sequence evolution. However, secondary structure elements with important function are stabilized by higher guanosine content that allows regions of structure to persist as sequence evolution proceeds, and, within the confines of selective pressure, allows structures to evolve.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Gorelick is employed by a private company (SAIC-Frederick, Inc.), but he is employed to perform basic research, under contract to the National Cancer Institute, and his work has no connection with any product-development or other commercial activities. This has no bearing on employment, consultancy, patents, products in development or marketed products etc. In addition, this affiliation does not alter our adherence to all of the PLoS Pathogens policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
References
-
- Olsen HS, Nelbock P, Cochrane AW, Rosen CA (1990) Secondary structure is the major determinant for interaction of HIV rev protein with RNA. Science 247: 845–848. - PubMed
-
- Karn J (1999) Tackling Tat. J Mol Biol 293: 235–254. - PubMed
-
- Muesing MA, Smith DH, Capon DJ (1987) Regulation of mRNA accumulation by a human immunodeficiency virus trans-activator protein. Cell 48: 691–701. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 AI007001/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI068462/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016086/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37-AI044667/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI50410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI044667/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K12 GM088033/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AI068462/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001C/RC/CCR NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001E/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32-AI07001/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA16086/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

