Functional IL6R 358Ala allele impairs classical IL-6 receptor signaling and influences risk of diverse inflammatory diseases
- PMID: 23593036
- PMCID: PMC3617094
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003444
Functional IL6R 358Ala allele impairs classical IL-6 receptor signaling and influences risk of diverse inflammatory diseases
Abstract
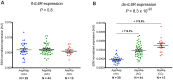
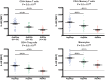
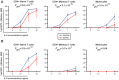
Inflammation, which is directly regulated by interleukin-6 (IL-6) signaling, is implicated in the etiology of several chronic diseases. Although a common, non-synonymous variant in the IL-6 receptor gene (IL6R Asp358Ala; rs2228145 A>C) is associated with the risk of several common diseases, with the 358Ala allele conferring protection from coronary heart disease (CHD), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), atrial fibrillation (AF), abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), and increased susceptibility to asthma, the variant's effect on IL-6 signaling is not known. Here we provide evidence for the association of this non-synonymous variant with the risk of type 1 diabetes (T1D) in two independent populations and confirm that rs2228145 is the major determinant of the concentration of circulating soluble IL-6R (sIL-6R) levels (34.6% increase in sIL-6R per copy of the minor allele 358Ala; rs2228145 [C]). To further investigate the molecular mechanism of this variant, we analyzed expression of IL-6R in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) in 128 volunteers from the Cambridge BioResource. We demonstrate that, although 358Ala increases transcription of the soluble IL6R isoform (P = 8.3×10⁻²²) and not the membrane-bound isoform, 358Ala reduces surface expression of IL-6R on CD4+ T cells and monocytes (up to 28% reduction per allele; P≤5.6×10⁻²²). Importantly, reduced expression of membrane-bound IL-6R resulted in impaired IL-6 responsiveness, as measured by decreased phosphorylation of the transcription factors STAT3 and STAT1 following stimulation with IL-6 (P≤5.2×10⁻⁷). Our findings elucidate the regulation of IL-6 signaling by IL-6R, which is causally relevant to several complex diseases, identify mechanisms for new approaches to target the IL-6/IL-6R axis, and anticipate differences in treatment response to IL-6 therapies based on this common IL6R variant.
Conflict of interest statement
AM is a full time employee of Pfizer. JD has received research funding from the British Heart Foundation; BUPA Foundation; Denka; diaDexus; European Union; European Research Council; Evelyn Trust; Fogarty International Centre; GlaxoSmithKline; Medical Research Council; Merck Sharp and Dohme; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke; National Institute for Health Research; Novartis; Pfizer; Roche; Wellcome Trust; and UK Biobank; and has served on advisory boards for Merck, Pfizer, and Novartis, for which he has received compensation. All other authors have declared that no competing interest exist.
Figures

References
-
- Van Snick J (1990) Interleukin-6: An Overview. Annual Review of Immunology 8: 253–278. - PubMed
-
- Neurath MF, Finotto S (2011) IL-6 signaling in autoimmunity, chronic inflammation and inflammation-associated cancer. Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews 22: 83–89. - PubMed
-
- Kallen K-J (2002) The role of transsignalling via the agonistic soluble IL-6 receptor in human diseases. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research 1592: 323–343. - PubMed
-
- Chalaris A, Garbers C, Rabe B, Rose-John S, Scheller J (2011) The soluble Interleukin 6 receptor: Generation and role in inflammation and cancer. European Journal of Cell Biology 90: 484–494. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RG/08/014/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- 068545/Z/02/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- RG/08/014/24067/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- 096388/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- MR/L003120/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 DK062418/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 100140/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0000934/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 076113/C/04/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 091157/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 061858/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

