Interaction between HLA-DRB1-DQB1 haplotypes in Sardinian multiple sclerosis population
- PMID: 23593151
- PMCID: PMC3620236
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059790
Interaction between HLA-DRB1-DQB1 haplotypes in Sardinian multiple sclerosis population
Abstract
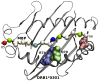
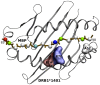
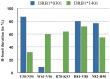
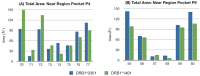
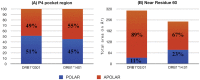
We performed a case-control study in 2,555 multiple sclerosis (MS) Sardinian patients and 1,365 healthy ethnically matched controls, analyzing the interactions between HLA-DRB1-DQB1 haplotypes and defining a rank of genotypes conferring a variable degree of risk to the disease. Four haplotypes were found to confer susceptibility (*13:03-*03:01 OR = 3.3, Pc 5.1 × 10(-5), *04:05-*03:01 OR = 2.1, Pc 9.7 × 10(-8), *15:01-*06:02 OR = 2.0, Pc = 9.1 × 10(-3), *03:01-*02:01 OR = 1.7 Pc = 7.9 × 10(-22)) and protection (*11, OR = 0.8, Pc = 2.7 × 10(-2), *16:01-*05:02 OR = 0.6, Pc = 4.8 × 10(-16), *14:01-4-*05:031 = OR = 0.5, Pc = 9.8 × 10(-4) and *15:02-*06:01 OR = 0.4, Pc = 5.1 × 10(-4)). The relative predispositional effect method confirms all the positively associated haplotypes and showed that also *08 and *04 haplotypes confers susceptibility, while the *11 was excluded as protective haplotype. Genotypic ORs highlighted two typologies of interaction between haplotypes: i) a neutral interaction, in which the global risk is coherent with the sum of the single haplotype risks; ii) a negative interaction, in which the genotypic OR observed is lower than the sum of the OR of the two haplotypes. The phylogenic tree of the MS-associated DRB1 alleles found in Sardinian patients revealed a cluster represented by *14:01, *04:05, *13∶03, *08:01 and *03:01 alleles. Sequence alignment analysis showed that amino acids near pocket P4 and pocket P9 differentiated protective from predisposing alleles under investigation. Furthermore, molecular dynamics simulation performed on alleles revealed that position 70 is crucial in binding of MBP 85-99 peptide. All together, these data suggest that propensity to MS observed in Sardinian population carried by the various HLA-DRB1-DQB1 molecules can be due to functional peculiarity in the antigen presentation mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Compston A, Coles A (2008) Multiple sclerosis. Lancet 372, 1502–1517. - PubMed
-
- Ebers GC, Sadovnick AD, Risch NJ (1995) the Canadian Collaborative Study Group (1995) A genetic basis for familial aggregation in multiple sclerosis. Nature 377: 150–151. - PubMed
-
- Ballerini C, Guerini FR, Rombolà G, Rosati E, Massacesi L, et al. (2004) HLA-multiple sclerosis association in continental Italy and correlation with disease prevalence in Europe. J Neuroimmunol 150: 178–185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

