ERCC1 and ERCC2 haplotype modulates induced BPDE-DNA adducts in primary cultured lymphocytes
- PMID: 23593158
- PMCID: PMC3617188
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060006
ERCC1 and ERCC2 haplotype modulates induced BPDE-DNA adducts in primary cultured lymphocytes
Abstract
Background: Benzo[a]pyrene(B[a]P), and its ultimate metabolite Benzo[a]pyrene 7,8-diol 9,10-epoxide (BPDE), are classic DNA damaging carcinogens. DNA damage caused by BPDE is normally repaired by Nucleotide Excision Repair (NER), of which ERCC1 and ERCC2/XPD exert an indispensable role. Genetic variations in ERCC1 and ERCC2 have been related to DNA repair efficiency. In this study we used lymphocytes from healthy individuals to show that polymorphisms in ERCC1 and ERCC2 are directly associated with decreased DNA repair efficiency.
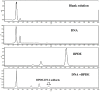
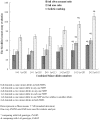
Methods: ERCC1 (rs3212986 and rs11615) and ERCC2 (rs13181, rs1799793 and rs238406) were genotyped in 818 healthy Han individuals from the northeast of China. BPDE induced DNA adducts in lymphocytes were assessed by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) in 282 randomly selected participants. The effect of ERCC1 rs3212986 and ERCC2 rs238406 on DNA damage caused by B[a]P was assessed with a modified comet assay.
Results: We found that the variant genotypes of ERCC1 rs3212986 and ERCC2 rs238406 were associated with the high levels of BPDE-DNA adducts. Especially ERCC1 rs3212986 A-allele variant was significantly associated with the high BPDE-DNA adducts. Haplotype analysis showed that the ERCC1 haplotype AC (OR = 2.36, 95% CI = 1.84-2.97), ERCC2 haplotype AGA (OR = 1.51, 95% CI = 1.06-2.15) and haplotype block AGAAC (OR = 5.28, 95% CI = 2.95-9.43), AGCAC (OR = 1.35 95% CI = 1.13-1.60) were linked with high BPDE-DNA adducts. In addition, we found that the combined minor alleles of ERCC1 rs3212986 and ERCC2 rs238406 were associated with a reduced DNA repair capacity.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that the variant genotypes of ERCC1 rs3212986 and ERCC2 rs238406 are associated with decreased repair efficiency of BPDE induced DNA damage, and may be predictive for an individual's DNA repair capacity in response to environmental carcinogens.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genotypes and haplotypes of ERCC1 and ERCC2/XPD genes predict levels of benzo[a]pyrene diol epoxide-induced DNA adducts in cultured primary lymphocytes from healthy individuals: a genotype-phenotype correlation analysis.Carcinogenesis. 2008 Aug;29(8):1560-6. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgn089. Epub 2008 Jul 16. Carcinogenesis. 2008. PMID: 18635523 Free PMC article.
-
Excision repair of BPDE-adducts in human lymphocytes: diminished capacity associated with ERCC1 C8092A (rs3212986) polymorphism.Arch Toxicol. 2013 Apr;87(4):699-709. doi: 10.1007/s00204-012-0986-0. Epub 2012 Dec 1. Arch Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23203453
-
Genetic polymorphisms in 19q13.3 genes associated with alteration of repair capacity to BPDE-DNA adducts in primary cultured lymphocytes.Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2016 Dec;812:39-47. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2016.10.004. Epub 2016 Oct 29. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2016. PMID: 27908386
-
Association between common polymorphisms in ERCC gene and glioma risk: A meta-analysis of 15 studies.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 May;96(20):e6832. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006832. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28514298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA Repair Genetics and the Risk of Radiation Pneumonitis in Patients With Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2024 Jul;36(7):e182-e196. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2024.03.019. Epub 2024 Mar 24. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2024. PMID: 38653664
Cited by
-
Excision Repair Cross Complementation Group 1 Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Nivolumab in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Front Oncol. 2020 Sep 2;10:1167. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01167. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32983959 Free PMC article.
-
Alteration of the Nucleotide Excision Repair (NER) Pathway in Soft Tissue Sarcoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 28;23(15):8360. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158360. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955506 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphisms in ERCC1 and ERCC2/XPD genes and carcinogen DNA adducts in human lung.Lung Cancer. 2015 Jul;89(1):8-12. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2015.05.001. Epub 2015 May 11. Lung Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26001533 Free PMC article.
-
The Association of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism rs13181 in ERCC2 with Risk and Prognosis of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in an Endemic Chinese Population.Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2021 Mar 17;14:359-367. doi: 10.2147/PGPM.S296215. eCollection 2021. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 33762840 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of ERCC1 (rs3212986) and ERCC2 (rs1799793, rs13181) polymorphisms of DNA repair genes in breast cancer occurrence in Burkina Faso.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2023 Apr;11(4):e2134. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.2134. Epub 2023 Jan 3. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2023. PMID: 36594475 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jernstrom B, Graslund A (1994) Covalent binding of benzo[a]pyrene 7,8-dihydrodiol 9,10-epoxides to DNA: molecular structures, induced mutations and biological consequences. Biophys Chem 49: 185–99. - PubMed
-
- Haugen A, Becher G, Benestad C, Vahakangas K, Trivers GE, et al. (1986) Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the urine, benzo(a) pyrene diol epoxide-DNA adducts in lymphocyte DNA, and antibodies to the adducts in sera from coke oven workers exposed to measured amounts of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the work atmosphere. Cancer Res 46(8): 4178–4183. - PubMed
-
- Miller EC (1978) Some current perspectives on chemical carcinogenesis in humans and experimental animals: presidential address. Cancer Res 38(6): 1479–1496. - PubMed
-
- Vineis P, Manuguerra M, Kavvoura FK, Guarrera S, Allione A, et al. (2009) A field synopsis on low- penetrance variants in DNA repair genes and cancer susceptibility. J Natl Cancer Inst 101(1): 24–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

