Willin, an upstream component of the hippo signaling pathway, orchestrates mammalian peripheral nerve fibroblasts
- PMID: 23593160
- PMCID: PMC3620498
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060028
Willin, an upstream component of the hippo signaling pathway, orchestrates mammalian peripheral nerve fibroblasts
Abstract
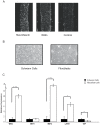
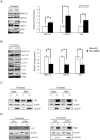
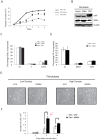
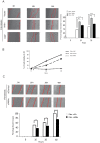
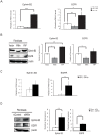
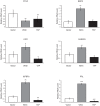
Willin/FRMD6 was first identified in the rat sciatic nerve, which is composed of neurons, Schwann cells, and fibroblasts. Willin is an upstream component of the Hippo signaling pathway, which results in the inactivation of the transcriptional co-activator YAP through Ser127 phosphorylation. This in turn suppresses the expression of genes involved in cell growth, proliferation and cancer development ensuring the control of organ size, cell contact inhibition and apoptosis. Here we show that in the mammalian sciatic nerve, Willin is predominantly expressed in fibroblasts and that Willin expression activates the Hippo signaling cascade and induces YAP translocation from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. In addition within these cells, although it inhibits cellular proliferation, Willin expression induces a quicker directional migration towards scratch closure and an increased expression of factors linked to nerve regeneration. These results show that Willin modulates sciatic nerve fibroblast activity indicating that Willin may have a potential role in the regeneration of the peripheral nervous system.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Willin/FRMD6 expression activates the Hippo signaling pathway kinases in mammals and antagonizes oncogenic YAP.Oncogene. 2012 Jan 12;31(2):238-50. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.224. Epub 2011 Jun 13. Oncogene. 2012. PMID: 21666719
-
KIBRA exhibits MST-independent functional regulation of the Hippo signaling pathway in mammals.Oncogene. 2013 Apr 4;32(14):1821-30. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.196. Epub 2012 May 21. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 22614006
-
Elevated expression of Par3 promotes prostate cancer metastasis by forming a Par3/aPKC/KIBRA complex and inactivating the hippo pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Oct 10;36(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0609-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 29017577 Free PMC article.
-
The Hippo pathway: Horizons for innovative treatments of peripheral nerve diseases.J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2021 Mar;26(1):4-16. doi: 10.1111/jns.12431. Epub 2021 Jan 23. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2021. PMID: 33449435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Willin/FRMD6: A Multi-Functional Neuronal Protein Associated with Alzheimer's Disease.Cells. 2021 Nov 4;10(11):3024. doi: 10.3390/cells10113024. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831245 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Allergic Rhinitis in Preschool Children and the Clinical Utility of FeNO.Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017 Jul;9(4):314-321. doi: 10.4168/aair.2017.9.4.314. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017. PMID: 28497918 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal myelin elongation relies on YAP activation by axonal growth and inhibition by Crb3/Hippo pathway.Nat Commun. 2016 Jul 20;7:12186. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12186. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27435623 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of genetic variations, differential gene expression, and allele-specific expression on metformin response in drug-naïve type 2 diabetes.J Endocrinol Invest. 2023 Jun;46(6):1205-1218. doi: 10.1007/s40618-022-01989-y. Epub 2022 Dec 18. J Endocrinol Invest. 2023. PMID: 36528847 Free PMC article.
-
The Angiomotins--from discovery to function.FEBS Lett. 2014 Aug 19;588(16):2693-703. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2014.02.006. Epub 2014 Feb 15. FEBS Lett. 2014. PMID: 24548561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression and regulation of FRMD6 in mouse DRG neurons and spinal cord after nerve injury.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 5;10(1):1880. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58261-7. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32024965 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

