Neurocognitive function in acromegaly after surgical resection of GH-secreting adenoma versus naïve acromegaly
- PMID: 23593161
- PMCID: PMC3617159
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060041
Neurocognitive function in acromegaly after surgical resection of GH-secreting adenoma versus naïve acromegaly
Abstract
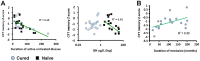
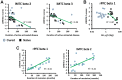
Patients with active untreated acromegaly show mild to moderate neurocognitive disorders that are associated to chronic exposure to growth hormone (GH) and insulin-like growth factor (IGF-I) hypersecretion. However, it is unknown whether these disorders improve after controlling GH/IGF-I hypersecretion. The aim of this study was to compare neurocognitive functions of patients who successfully underwent GH-secreting adenoma transsphenoidal surgery (cured patients) with patients with naive acromegaly. In addition, we wanted to determine the impact of different clinical and biochemical variables on neurocognitive status in patients with active disease and after long-term cure. A battery of six standardized neuropsychological tests assessed attention, memory and executive functioning. In addition, a quantitative electroencephalography with Low-Resolution Electromagnetic Tomography (LORETA) solution was performed to obtain information about the neurophysiological state of the patients. Neurocognitive data was compared to that of a healthy control group. Multiple linear regression analysis was also conducted using clinical and hormonal parameters to obtain a set of independent predictors of neurocognitive state before and after cure. Both groups of patients scored significantly poorer than the healthy controls on memory tests, especially those assessing visual and verbal recall. Patients with cured acromegaly did not obtain better cognitive measures than naïve patients. Furthermore memory deficits were associated with decreased beta activity in left medial temporal cortex in both groups of patients. Regression analysis showed longer duration of untreated acromegaly was associated with more severe neurocognitive complications, regardless of the diagnostic group, whereas GH levels at the time of assessment was related to neurocognitive outcome only in naïve patients. Longer duration of post-operative biochemical remission of acromegaly was associated with better neurocognitive state. Overall, this data suggests that the effects of chronic exposure to GH/IGF-I hypersecretion could have long-term effects on brain functions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Colao A, Ferone D, Marzullo P, Lombardi G (2004) Systemic complications of acromegaly: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and management. Endocr Rev 25: 102–152. - PubMed
-
- Melmed S (2006) Acromegaly. N Engl J Med. 355: 2558–2573. - PubMed
-
- Tanriverdi F, Yapislar H, Karaca Z, Unluhizarci K, Suer C, et al. (2009) Evaluation of cognitive performance by using P300 auditory event related potentials (ERPs) in patients with growth hormone (GH) deficiency and acromegaly. Growth Horm IGF Res 19: 24–30. - PubMed
-
- Leon-Carrion J, Martin-Rodriguez JF, Madrazo-Atutxa A, Soto-Moreno A, Venegas-Moreno E, et al. (2010) Evidence of cognitive and neurophysiological impairment in patients with untreated naïve acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95: 4367–4379. - PubMed
-
- Sievers C, Sämann PG, Pfister H, Dimopoulou C, Czisch M, et al. (2012) Cognitive function in acromegaly: description and brain volumetric correlates. Pituitary 15: 350–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

