Association between subcortical vascular lesion location and cognition: a voxel-based and tract-based lesion-symptom mapping study. The SMART-MR study
- PMID: 23593238
- PMCID: PMC3620525
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060541
Association between subcortical vascular lesion location and cognition: a voxel-based and tract-based lesion-symptom mapping study. The SMART-MR study
Abstract
Introduction: Lacunar lesions (LLs) and white matter lesions (WMLs) affect cognition. We assessed whether lesions located in specific white matter tracts were associated with cognitive performance taking into account total lesion burden.
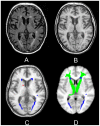
Methods: Within the Second Manifestations of ARTerial disease Magnetic Resonance (SMART-MR) study, cross-sectional analyses were performed on 516 patients with manifest arterial disease. We applied an assumption-free voxel-based lesion-symptom mapping approach to investigate the relation between LL and WML locations on 1.5 Tesla brain MRI and compound scores of executive functioning, memory and processing speed. Secondly, a multivariable linear regression model was used to relate the regional volume of LLs and WMLs within specific white matter tracts to cognitive functioning.
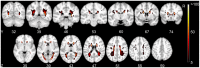
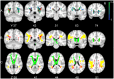
Results: Voxel-based lesion-symptom mapping identified several clusters of voxels with a significant correlation between WMLs and executive functioning, mostly located within the superior longitudinal fasciculus and anterior thalamic radiation. In the multivariable linear regression model, a statistically significant association was found between regional LL volume within the superior longitudinal fasciculus and anterior thalamic radiation and executive functioning after adjustment for total LL and WML burden.
Conclusion: These findings identify the superior longitudinal fasciculus and anterior thalamic radiation as key anatomical structures in executive functioning and emphasize the role of strategically located vascular lesions in vascular cognitive impairment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Strategic role of frontal white matter tracts in vascular cognitive impairment: a voxel-based lesion-symptom mapping study in CADASIL.Brain. 2011 Aug;134(Pt 8):2366-75. doi: 10.1093/brain/awr169. Epub 2011 Jul 14. Brain. 2011. PMID: 21764819
-
Impact of Strategically Located White Matter Hyperintensities on Cognition in Memory Clinic Patients with Small Vessel Disease.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 8;11(11):e0166261. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166261. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27824925 Free PMC article.
-
Strategic white matter hyperintensity locations for cognitive impairment: A multicenter lesion-symptom mapping study in 3525 memory clinic patients.Alzheimers Dement. 2023 Jun;19(6):2420-2432. doi: 10.1002/alz.12827. Epub 2022 Dec 12. Alzheimers Dement. 2023. PMID: 36504357
-
White matter tracts and executive functions: a review of causal and correlation evidence.Brain. 2024 Feb 1;147(2):352-371. doi: 10.1093/brain/awad308. Brain. 2024. PMID: 37703295 Review.
-
Imaging of static brain lesions in vascular dementia: implications for clinical trials.Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 1999 Oct-Dec;13 Suppl 3:S81-90. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 1999. PMID: 10609686 Review.
Cited by
-
Apolipoprotein E-dependent load of white matter hyperintensities in Alzheimer's disease: a voxel-based lesion mapping study.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2015 May 15;7(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s13195-015-0111-8. eCollection 2015. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 25984242 Free PMC article.
-
BIANCA (Brain Intensity AbNormality Classification Algorithm): A new tool for automated segmentation of white matter hyperintensities.Neuroimage. 2016 Nov 1;141:191-205. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.07.018. Epub 2016 Jul 9. Neuroimage. 2016. PMID: 27402600 Free PMC article.
-
Strategic white matter tracts for processing speed deficits in age-related small vessel disease.Neurology. 2014 Jun 3;82(22):1946-50. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000475. Epub 2014 May 2. Neurology. 2014. PMID: 24793184 Free PMC article.
-
Brain structure and verbal function across adulthood while controlling for cerebrovascular risks.Hum Brain Mapp. 2017 Jul;38(7):3472-3490. doi: 10.1002/hbm.23602. Epub 2017 Apr 8. Hum Brain Mapp. 2017. PMID: 28390167 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of white matter hyperintensities on structural connectivity and cognition in cognitively intact ADNI participants.Neurobiol Aging. 2024 Mar;135:79-90. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2023.10.012. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Neurobiol Aging. 2024. PMID: 38262221 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tatemichi TK, Desmond DW, Paik M, Figueroa M, Gropen TI, et al. (1993) Clinical determinants of dementia related to stroke. Ann Neurol 33: 568–575. - PubMed
-
- Pohjasvaara T, Erkinjuntti T, Ylikoski R, Hietanen M, Vataja R, et al. (1998) Clinical determinants of poststroke dementia. Stroke 29: 75–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

